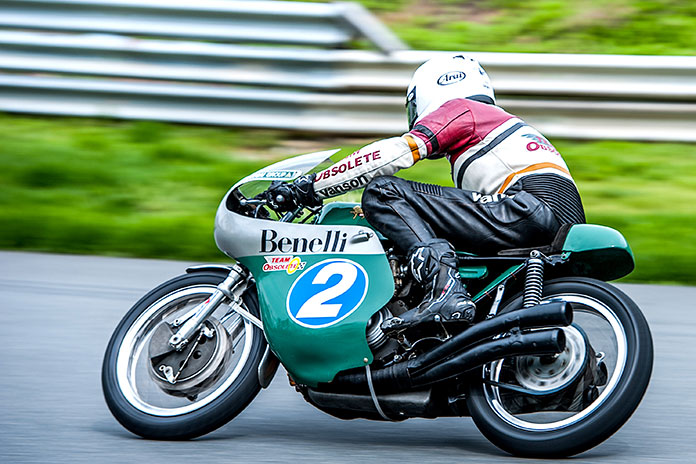
Benelli wasn’t the first motorcycle manufacturer in Italy, but it’s the oldest Italian brand that still makes motorcycles, though its production history had some interruptions. As was the case in the United States, there were scores of upstart motorcycle manufacturers in Italy in the early decades of the 20th century, but only a handful survived. Join us for a 111-year walk down the annals of Italian motorcycle history.
The Benelli Early Years: 1911-1937

In 1911, the six Benelli brothers opened their first shop in Pesaro, Italy. The Benelli Garage serviced and repaired bicycles and motorcycles, made spare parts for both, and within a few years set to work on their own engine design. A 75cc 2-stroke Single debuted in 1920, and their first complete motorcycle followed a year later.
In 1927, Benelli introduced a 175cc 4-stroke Single with what would become the company’s characteristic “cascade”-type overhead-cam system. Designed by the eldest brother, Giuseppe, the gear-driven OHC engine powered the youngest brother, Antonino, to four national championships in the Italian long-distance roadraces.
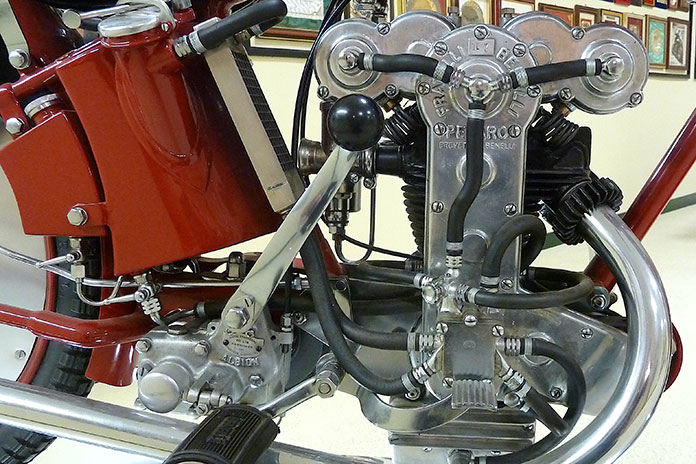
By 1931, the road models were selling well, and the widow Signora Teresa Benelli believed that investing most of her late husband’s estate in the boys’ motorcycle venture had been worthwhile. The prospects for continued growth looked good. A larger factory opened in 1934, and new 250cc and 500cc engines entered production.
Antonino’s racing success fueled the development of the single- and double-overhead cam engines, but his career ended with a crash in the 1932 Grand Prix at the Circuit del Tiguillia. After a long convalescence, he rejoined the family business. Unfortunately, Antonino died in a road accident in 1937 at the age of 34, just a few weeks after the company also lost the head of the experimental department, Otello Giovanardi, who was killed while testing the new 500cc racebike on a road near the factory.
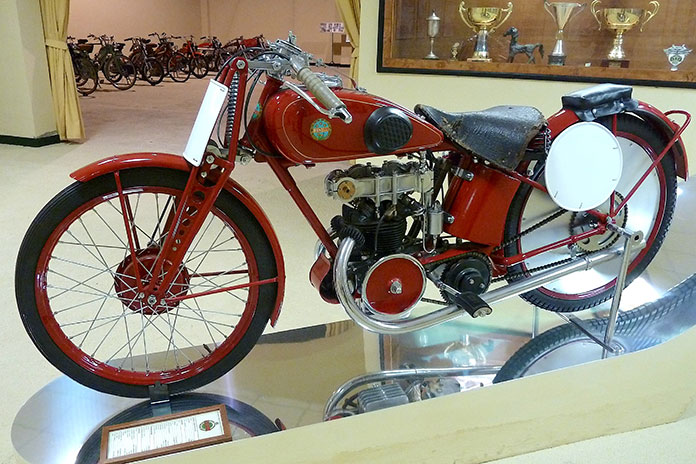

The War Years: 1939-1945
In the late 1930s, the long-standing rumors of war were turning into the realities of armed combat. Ted Mellors posted Benelli’s first Isle of Man TT victory in 1939 by winning the Lightweight class on the Single, and Benelli was developing a supercharged, liquid-cooled 250cc inline-Four claimed to produce 52 hp at 10,000 rpm, but the war preempted its planned 1940 introduction at the TT.
Benelli and Moto Guzzi, which also produced its first model in 1921, were direct competitors in the domestic motorcycle market, along with Gilera and Garelli. Ducati was still in the radio and electronics business and would enter the two-wheeled world after World War II, joined by Parilla, MV Agusta, and Aermacchi. In the 1940s and ’50s, market competition among the Italian, German, and English manufacturers picked up steam.
Benelli survived the first half of the war by building and supplying parts for the M36 three-wheeler, powered by a 500cc Single. Already adapted for military use, the trike was useful for moving supplies and ammunition to the battle lines, but by then, more than a few Italians had reason to doubt their choice of leadership, the socialist-turned-fascist Benito Mussolini. The trains no longer ran on time because Allied bombers had destroyed much of the tracks, as well as most of the factories supplying the Italian army with equipment and parts, including the Benelli plant.
Post-War Years: 1945-1959
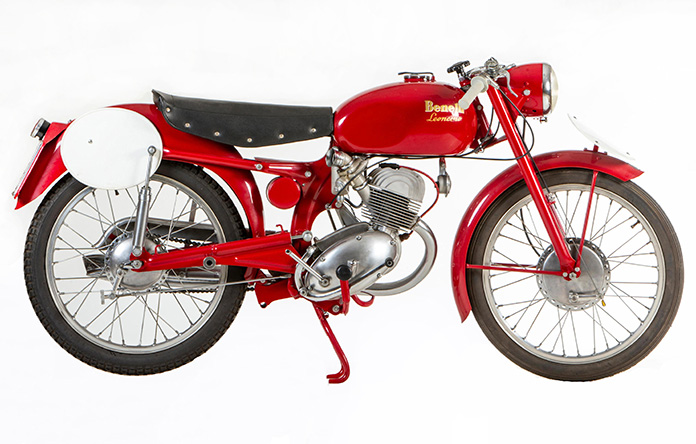

After the war, with what machinery and tooling had survived, Benelli resumed production with civilian versions of the trike and the pre-war road models. When racing resumed in 1947, plans were underway to return to the track the following season. In 1948, Benelli hired the dashing professional rider Dario Ambrosini, who went on to win the 250cc World Championship in 1950. His victory marked Benelli’s first world title, but another 19 years would pass before it would win another.
Despite their success in rebuilding the business and going racing, all was not biscotti and gelato among the brothers. Giuseppe, who was head designer/engineer at the time, was strongly committed to the racing program. The consensus among his siblings was less enthusiastic. The cost of competing against larger rivals like Moto Guzzi, Mondial, and Gilera was deemed excessive, so in 1949, Giuseppe parted ways with the family business and established his own company, Moto B Pesaro.
Later shortened to Motobi, the company built 2-stroke and 4-stroke Singles, shifting to 4-strokes exclusively in the mid-1950s. The distinctive egg-shaped horizontal cylinder preceded Aermacchi’s similar design. When Giuseppe died, leaving the company to his two sons, the marque was maintained for another five years. Motobi would be acquired by Benelli in 1962, putting it back in the family fold.
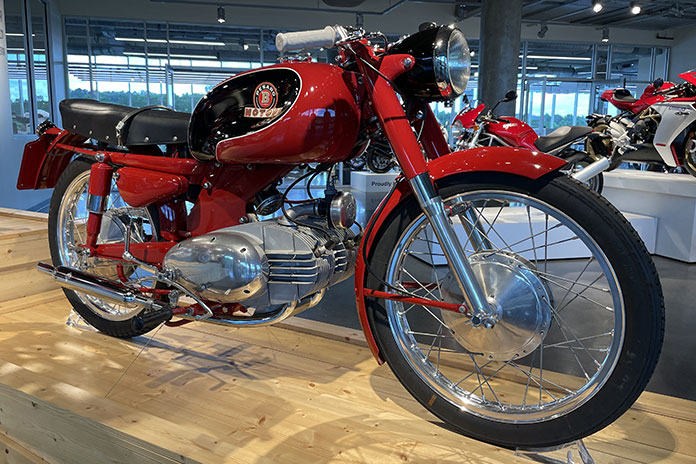

In 1950, with the second-eldest Benelli brother, Giovanni, at the helm, the company debuted the Leoncino 125cc 2-stroke, followed shortly by a 4-stroke of the same displacement. The “little lion” provided the backbone of the company’s sales for the next 20 years. Its credentials were posted solidly in 1953 when Leopoldo Tartarini won the first Motogiro d’Italia on the 2-stroke. Pesaro produced more than 50,000 of the various Leoncino models into the early ’70s.

Benelli was back to full production in the ’50s, with the Leoncino 125 2-stroke accounting for the most sales, followed by the 250cc Leonessa. Despite the declining overall market, a new 175cc OHC Single appeared in Touring and Sport versions in 1959. Grand Prix racing, on the other hand, had gotten ahead of itself in the 1950s. Streamlined, fully enclosed motorcycles were reaching speeds incompatible with the brake, suspension, and tire technology of the day. Fatalities rose accordingly, and after the “dustbin” fairings were banned in 1957, MV Agusta was the only Italian factory still competing in world championship races.
Related Story: 2021 Benelli Leoncino | Road Test Review
The Swingin’ Sixties
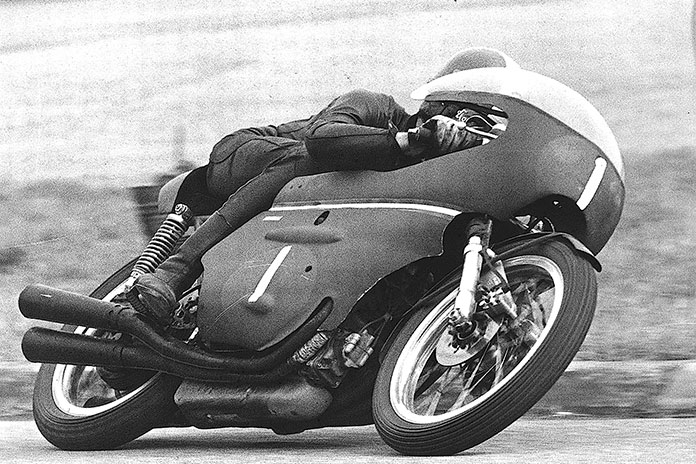
In the 1960s, Benelli decided to invest development in both utilitarian and recreational models for a wider market, including the United States. Slowing domestic sales pushed Pesaro to establish a distribution agreement with Cosmopolitan Motors of Pennsylvania and retail outlets in Montgomery Ward and JC Penney. Sold by Ward under the name Riverside, the 175cc 2-stroke and 250cc 4-stroke Singles were joined by the Cobra, a 125cc street scrambler. The product line was anchored at the bottom by minibikes, including the 65cc Dynamo and 180cc Volcano.
Its market expansion allowed Benelli to resume development of the 250cc OHC Four for racing. In 1965, Tarquino Provino won the Grand Prix at Monza, with Phil Read’s Yamaha second and another Benelli in third. A 16-valve 350cc model followed and carried Renzo Pasolini to victory at Modena, beating the mighty MV Agusta of Giacomo Agostini. Pasolini won the Italian championship in 1968 and finished second in the 1968 Grand Prix championship behind Agostini, with Kel Carruthers’ Aermacchi in third.
Impressed with his performance on the Aermacchi, Benelli hired Carruthers as Pasolini’s teammate on the 250 for the 1969 GP season. Both riders scored three wins, but it was Carruthers who collected Benelli’s second world championship, edging out Yamaha’s Kent Andersson.
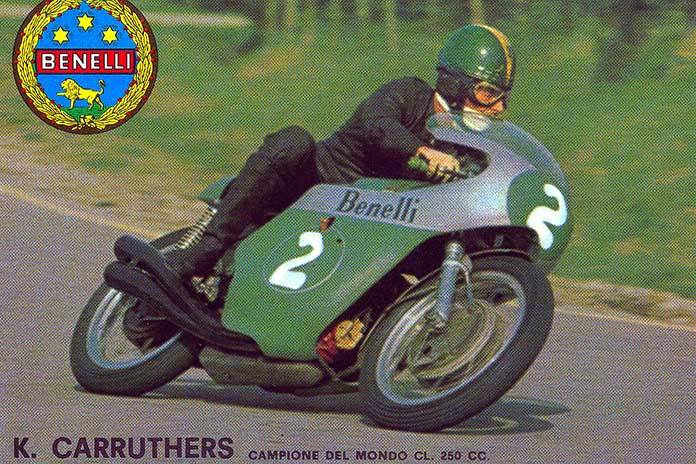
Pasolini and Carruthers both rode the 350 Benelli in the early GP rounds in 1970, but the series was dominated by MV’s Giacomo Agostini, who won nine of the 10 races. Pasolini switched to Aermacchi, then owned by Harley-Davidson, and Carruthers went to Yamaha. Finnish star Jarno Saarinen, who rode briefly for Benelli, also switched to Yamaha. The 2-stroke era had arrived.
Kel Carruthers, now 84, is best known in the U.S. for his early tutelage of future world champions Kenny Roberts and Eddie Lawson.
“Pasolini and I were to ride the 350s in 1970,” Carruthers recalls, “and I got second behind Agostini in Germany and Austria. I was running second behind him at the Isle of Man when the chain fell off. That’s when I decided to stick with Yamaha.”
His decision was confirmed when a strike at the Benelli factory meant that only Pasolini would get support.
Thus ended the 50-year racing chapter of Benelli history. Pesaro may have foreseen the coming 2-stroke domination of Grand Prix racing and possibly noted the general lack of interest in the sport among Americans. In either case, their double-barreled marketing approach in the U.S. had little connection with racing history.
With Cosmopolitan Motors as the distributor of bikes and parts to dealers and Montgomery Ward selling to the public, Benelli posted a broad lineup of road and dual-purpose models. The Riverside 125cc 2-stroke and 250cc 4-stroke Singles were offered in road and enduro models, and the minibikes were much cooler than the domestic Briggs & Stratton-powered counterparts.

At the lightweight end was the 125cc Cobra, based on the Leoncino, and the 250cc Barracuda with the horizontal cylinder of the Motobi. The Mojave 260/360 4-stroke Single was a stylish street scrambler/enduro. In 1968, the 250 Sport Special appeared with the Motobi engine, a long and slim tank, and clip-on handlebars. The Tornado 650 arrived in 1971, a handsome vertical-Twin with adequate power and reasonable comfort. The 2-strokes – 125, 175, and 250 – were available through the 1970s and joined by a brace of inline-Fours with 250cc and 500cc engines in 1975.
The Benelli Family Dynasty Ends: 1970-1989
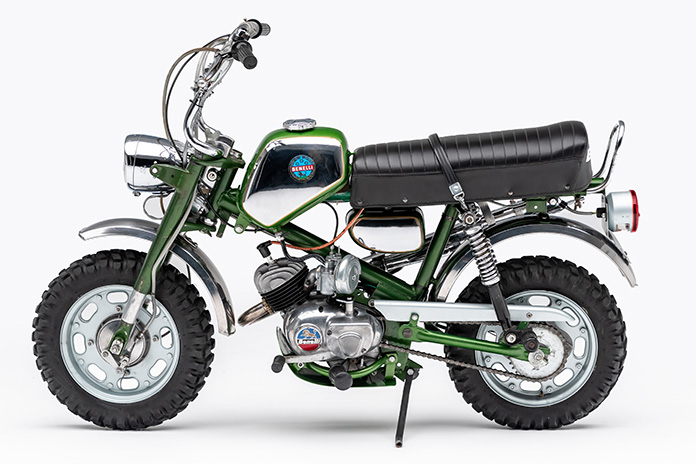

The return of the Fours marked the end of Benelli family ownership. While the British motorcycle industry was in decline, the Japanese had become the dominant international force in the market. In 1970, the Benelli heirs sold the business to Alejandro de Tomaso, the Argentinian racecar driver, builder, and creator of the mid-engine Mangusta sportscar, which evolved as the Ford Pantera. With the acquisition of Benelli (plus Moto Guzzi, Ghia bodyworks, and Maserati), de Tomaso was the de facto crown prince of Italian motorsports, outranked only by the king, Enzo Ferrari.
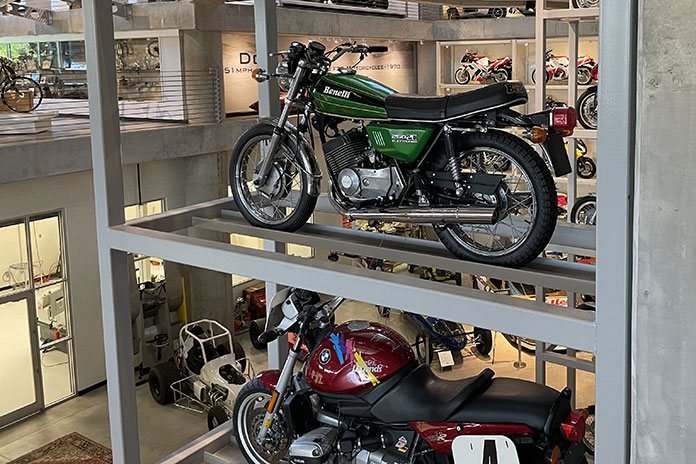

The design of the Benelli 500 Four borrowed heavily from the Honda engine, but the machine was rather chunky by comparison. The performance specs were roughly equivalent, but de Tomaso intended to do more than just match the Japanese multis. The feather in his cap was to be the Benelli Sei, the first 6-cylinder road model on the market. The Sei – basically the 500 Four with two more cylinders – weighed just over 500 lb, made about 70 hp, and emitted a lovely howl from the six exhaust pipes. Only 3,200 Sei 750s were produced between 1974 and 1978, the year Honda introduced the 1,047cc CBX Six. Benelli bored and stroked the Sei to 900cc, but less than 2,000 were built from 1979 to 1989.
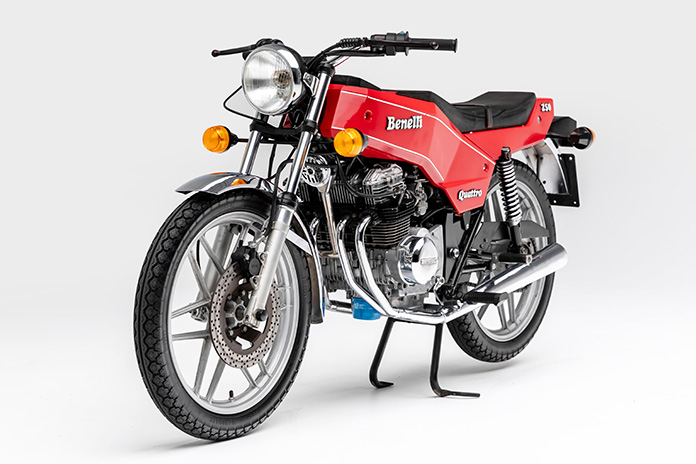

By the 1980s, Benelli had fallen further behind the curve. The combined effects of price, spotty distribution, and consistent improvement among the Japanese manufacturers effectively put Pesaro on the trailer. In 1989, Italian industrialist Giancarlo Seici attempted to revive the marque in the scooter market, to little avail.
The Modern Era: 1995-2022
In 1995, the Merloni Group bought the brand and hired young designers to create new models. A broad roster of scooters was joined by a 900cc 3-cylinder sportbike called the Tornado Tre, followed by the 1,130cc TNT Sport. Australia’s Peter Goddard campaigned the Triple in the 2001 and 2002 World Superbike series.
The encore performance for Benelli opened in 2005 when it was acquired by Qianjiang Motor Group of China, which was absorbed in 2015 by the Geely Holding Group (Volvo, Lotus, Proton, Terrafugia flying cars, etc.). Design and engineering facilities remain in Pesaro, while manufacturing and assembly are completed in Wenling, China. The plant produces more than a million vehicles a year and employs some 14,000 people.
The contemporary Benelli lineup continues the traditional framework of minibikes and middleweights but bears little resemblance to any models of the past. The TNT135 has an SOHC 4-valve Single with a dual-plug head, an oil cooler, and a 5-speed gearbox. With a trellis frame, a 41mm inverted fork, and racy slash-cut dual mufflers, the TNT is likely the sportiest minibike on the market. Its 65-mph top speed means it has no trouble keeping up with traffic, and its extra 10cc means it can outrun the popular Honda Grom.
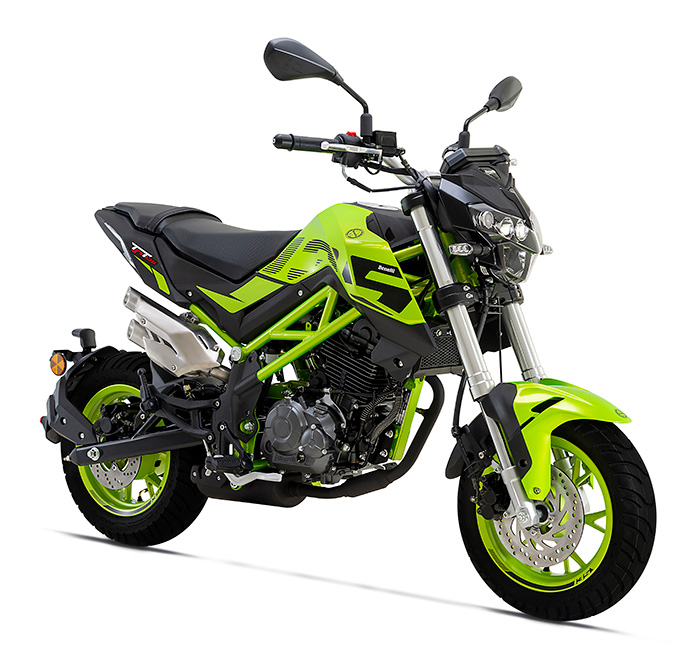

The 302S is a full-size motorcycle with a 38-hp, 300cc parallel-Twin, 17-inch wheels, and a 6-speed transmission. Like all the Benelli Twins, the 302 engine has a 360-degree crankshaft.
Up the displacement scale, the Leoncino in roadster and scrambler models has a 47-hp, 500cc parallel-Twin engine that makes 33 lb-ft of torque at 5,000 rpm. The Trail version gets slightly longer suspension travel, an inch more ground clearance, and a 19-inch front wheel.
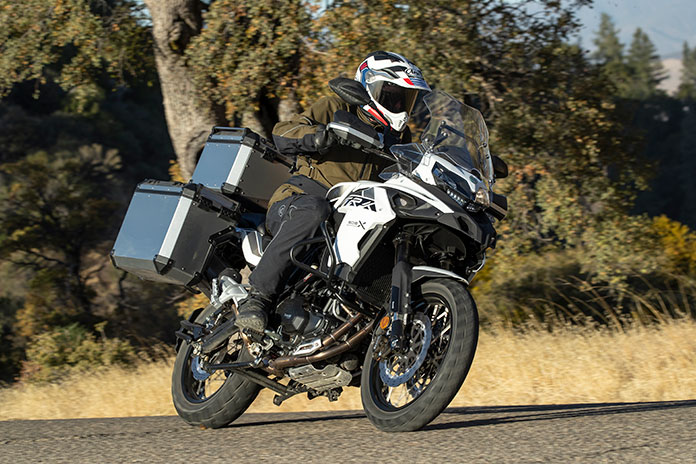
Benelli’s adventure models for the middleweight class, the TRK502 and TRK502X, employ the same liquid-cooled 500cc Twin, but the X adds a larger 5.3-gallon fuel tank and rebound-adjustable front fork. The X also gets an added inch of ground clearance, spoked wheels, a high-mount exhaust pipe, a 19-inch front wheel, and a 33-inch seat height – 1.5 inches taller than its stablemate.
Related Story: 2021 Benelli TRK502X | Road Test Review
There are too many variables to allow any reasonable forecast on the future of this marriage between Italian design and Chinese manufacturing. And that’s without counting the fractious political climate. The Pesaro/Wenling union may fare well enough without a substantial presence in the U.S., given their global market reach and potential cross-pollination of engineering and production advances from other brands in the Geely collective. Electric motorcycles are almost certainly in the pipeline.
In any case, the new Benellis mark another international design and manufacturing collaboration that puts to rest the old canard about Chinese build quality. A close look at the products, including the specs, fit and finish, welds, and warranties proves otherwise. And the fact that another venerable Italian marque has managed to survive in today’s hypercompetitive marketplace is cause for a measure of optimism. Viva Italia!
The post Tracing 111 years of Benelli history first appeared on Rider Magazine.
Source: RiderMagazine.com