
In July 2018, Harley-Davidson announced a five-year growth strategy called “More Roads to Harley-Davidson,” a plan to add new products, provide broader access, strengthen its dealer network and amplify the brand. Expansion beyond Harley’s typical cruiser, bagger and touring models would include the LiveWire electric motorcycle, which debuted for 2020, and “middleweight adventure touring, streetfighter and high-performance custom models.”
The “More Roads” strategy offered the first look at the Pan America adventure tourer, with few details beyond its displacement and what could be gleaned from a photo of the prototype. At the 2019 EICMA show in Milan, Harley unveiled the Pan America and the Bronx streetfighter, both to be powered by a liquid-cooled 60-degree V-twin engine platform called the Revolution Max — 1,250cc in the Pan America and 975cc in the Bronx — and launched in 2020.
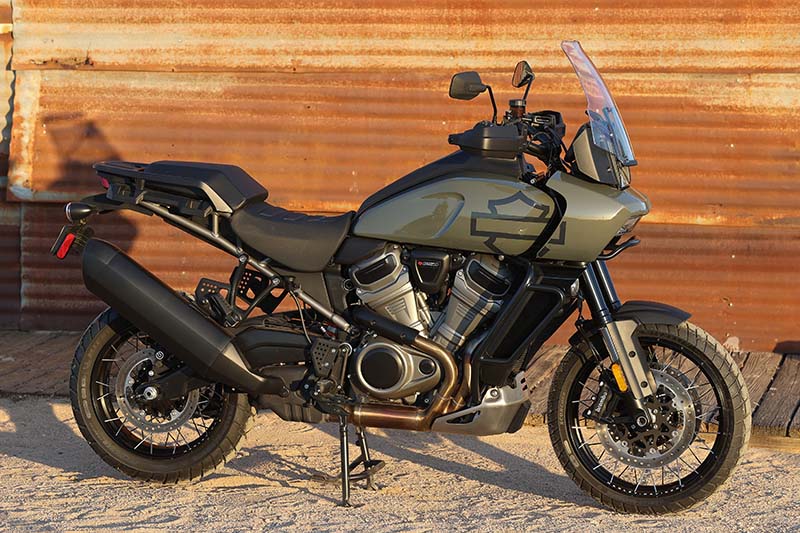
In February 2020, amid financial troubles, Harley-Davidson announced a revised five-year strategy called “Hardwire” that would, among other changes, “selectively focus on opportunities in profitable segments.” Plans to expand the company’s product portfolio were scaled back. The Pan America made the cut, the Bronx did not. Then the pandemic hit, which pushed the Pan America’s launch from late 2020 to early 2021. Details about the Pan America 1250 and up-spec Pan America 1250 Special were finally announced last February, and we got an opportunity to test ride the Special over two days in April.
Revolution Max 1250
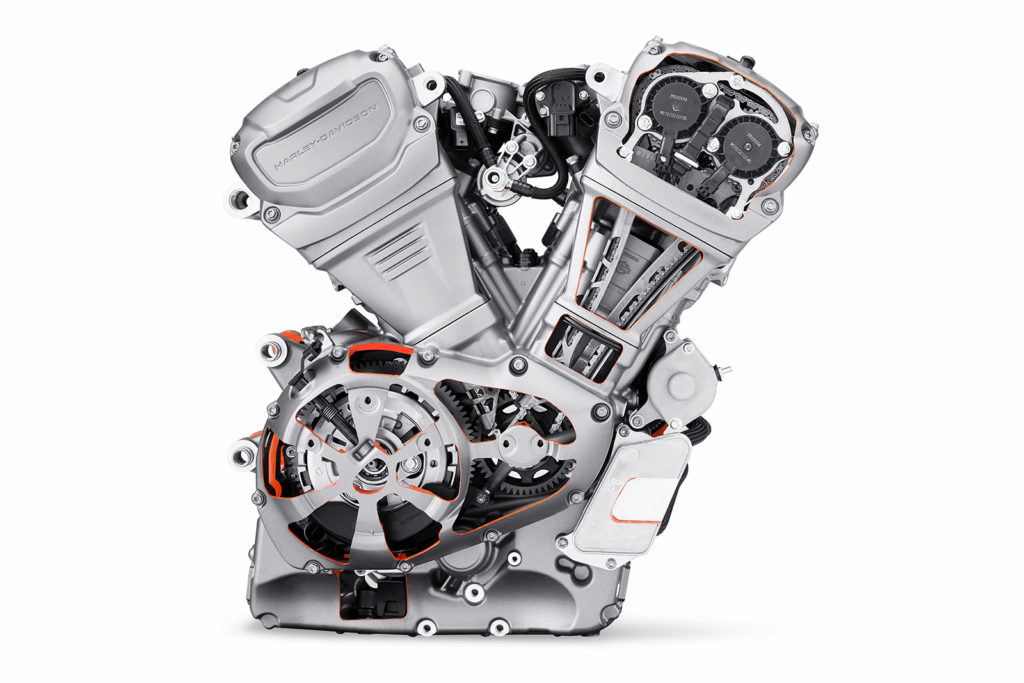

According to Harley, its all-new, modular Revolution Max engine will be offered in four displacements ranging from 500cc to 1,250cc. In addition to powering the Pan America, it will likely replace the aging, air-cooled mill in the Sportster and may replace the liquid-cooled Revolution X in whatever entry-level models fill the gap for the discontinued Street 500 and Street 750.
In the Pan America 1250, the Revolution Max displaces 1,252cc, has a 13.0:1 compression ratio and makes a claimed 150 horsepower at 9,000 rpm and 94 lb-ft of torque at 6,750 rpm. Like the Revolution V-twin that powered the V-Rod and the Revolution X that powered the Street models, the Max’s cylinders have a 60-degree included angle. The two crankshaft connecting rod journals are offset by 30 degrees, resulting in a 90-degree firing order for smooth power delivery. Dual overhead cams use roller-finger followers to actuate four valves per cylinder and hydraulic lash adjusters eliminate periodic maintenance. Computer-controlled variable valve timing (VVT) independently advances or retards intake and exhaust timing through a potential range of 40 degrees of crankshaft rotation, with the goal of broadening the powerband to deliver ample low-end torque as well as high-rpm horsepower. Dual spark plugs optimize ignition and a robust, dry-sump oiling system is designed to withstand the demands of adventure riding.
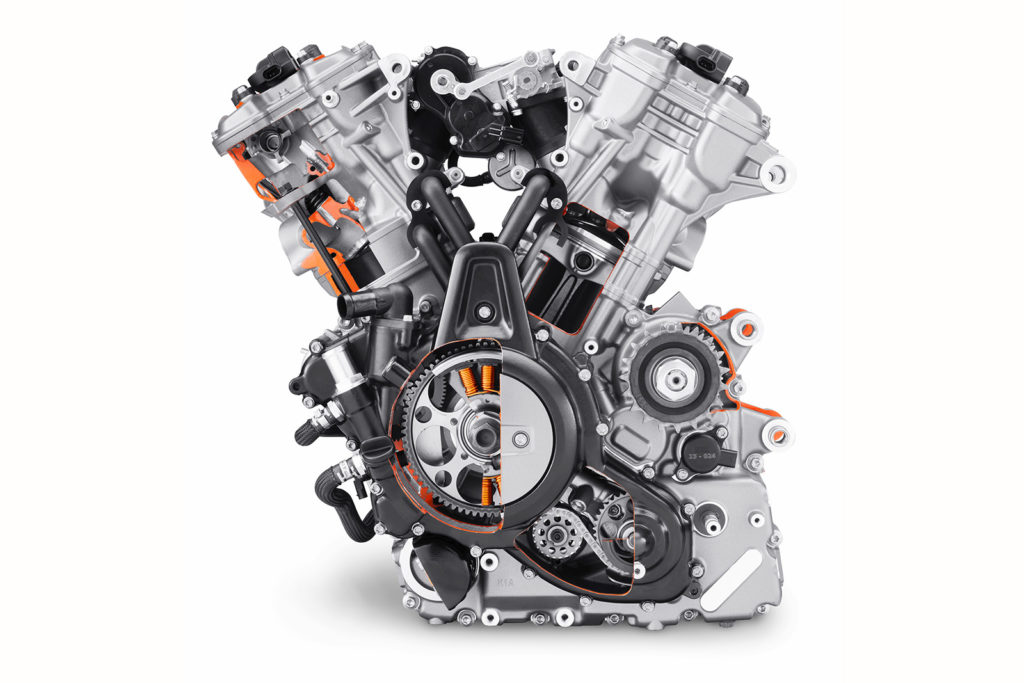

Because the Revolution Max is a stressed member of the Pan America’s chassis, it needed to be strong and light. Harley used finite element analysis and optimization techniques to reduce material mass in cast and molded components. Complex casting techniques allowed oil and coolant passages to be integrated into the engine in such a way that minimized wall thicknesses. Single-piece aluminum cylinders have nickel silicon carbide-surface galvanic coating, pistons are made of forged aluminum and the rocker, camshaft and primary covers are made of magnesium. An engine that vibrates less endures less stress over its life cycle, allowing components to be made lighter. A spiral-shaped, chain-driven balancer in the crankcase minimizes primary vibration, while a small balancer located in front of the cylinder head between the camshafts minimizes secondary vibration.
Revolution Max engines are built in Harley’s Pilgrim Road facility near Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and complete Pan Americas are assembled in York, Pennsylvania.
Adaptive Ride Height
To be competitive in the adventure touring segment, the Pan America 1250 and Pan America 1250 Special are equipped with state-of-the-art electronics like riding modes and Harley’s RDRS Safety Enhancements. The Special is equipped with added features, including Showa semi-active suspension that adjusts damping rates on the selected ride mode and automatically adjusts spring preload to provide 30% sag regardless of the load.
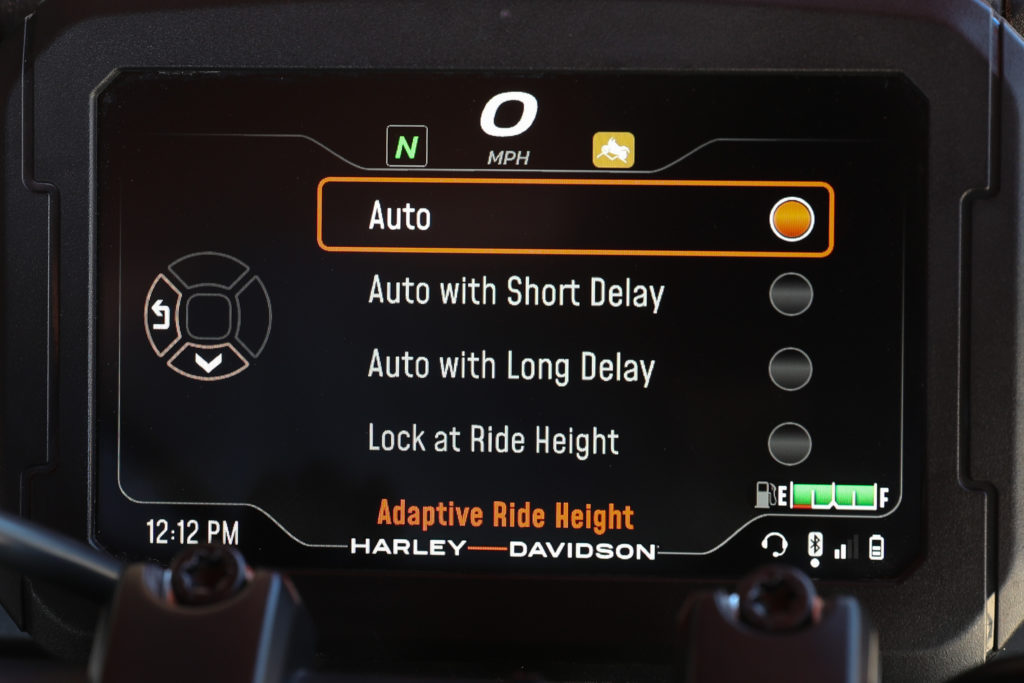
But the real innovation is the Adaptive Ride Height (ARH), a factory option available only on the Special. Using an array of sensors and algorithms, ARH automatically lowers the motorcycle’s ride height by 1 to 2 inches when the motorcycle comes to a stop (the amount of ride height adjustment depends on preload). Lowering the ride height lowers the rider’s seat, which accommodates a wider range of riders and adapts to a wider range of conditions than other full-sized adventure bikes, even those with semi-active suspension.
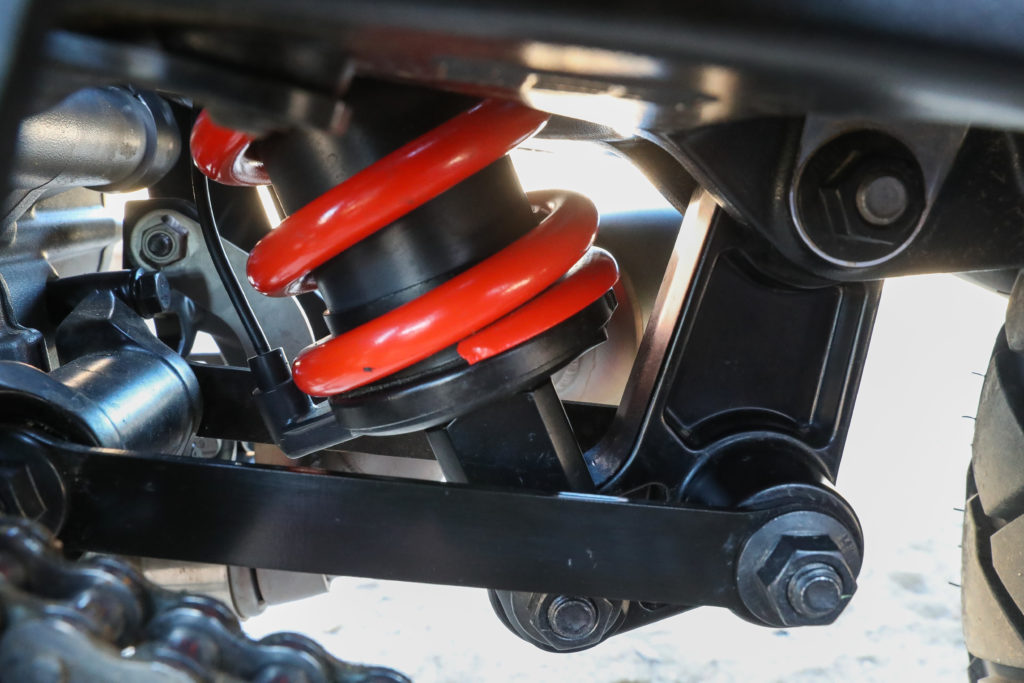

In standard ride modes, the default setting for ARH is Auto, but in custom ride modes ARH can be turned off or set to Auto with Short Delay or Auto with Long Delay, and those settings will be retained in that mode after the ignition is turned off. In Auto mode, ARH will not lower the motorcycle in an condition where speed is greater than 15.5 mph, but lowering could begin to occur at 15.5 mph if the rider is braking very hard. Speed, brake lever pressure and deceleration rate are all used to determine when to lower the motorcycle. ARH targets the bike to be lowered when the rider would typically be moving their feet off the pegs to put them on the ground, which typically happens at speeds much slower than 15.5 mph under casual braking.
In technical off-road conditions at low speeds, especially if there is a lot of stopping and starting involved, it may not be optimal to have the motorcycle repeatedly lower and raise itself. In Short Delay mode ARH will not lower the ride height at all until 0.5 second after the motorcycle comes to a stop. Long Delay mode waits until 2 seconds after coming to a stop before lowering the bike.
Since ARH is a factory-installed option, it cannot be added to a Pan America 1250 Special after purchase. The beauty of ARH is that it offers a lower seat height without reducing suspension travel or otherwise compromising the motorcycle’s performance or capabilities.
The post Tech Talk: Harley-Davidson Pan America 1250 first appeared on Rider Magazine.
Source: RiderMagazine.com
