Contributor Erik Slaven takes us on a ride through a century’s worth of history on supercharged and turbocharged motorcycles, the Wonder Twins of forced induction. –Ed.
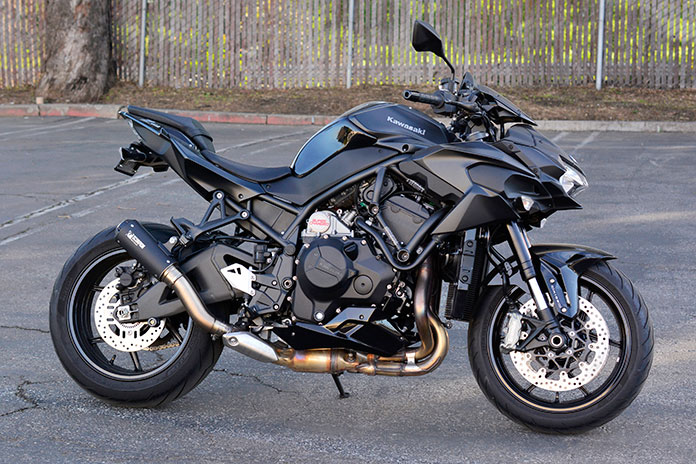
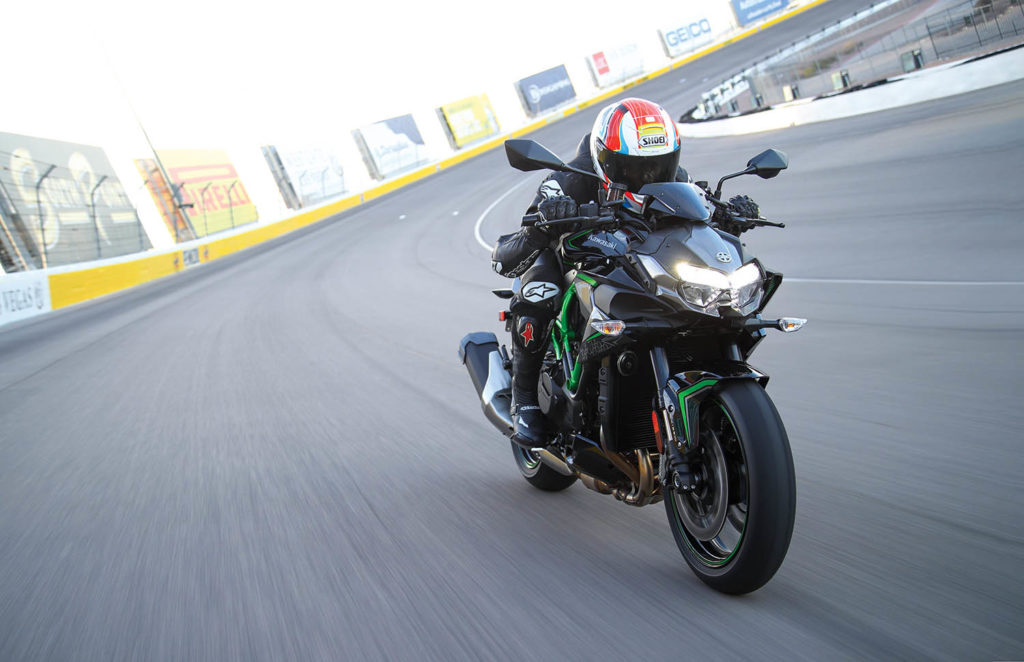
As a Kawasaki Z H2 owner, I can assure you that integrated superchargers are no gimmick. My Kawi is by far the fastest bike I’ve owned, and the sportier Ninja H2 is among the fastest street bikes ever produced. The BMW S 1000 RR, Ducati Panigale, and Suzuki Hayabusa show that naturally aspirated motorcycles are still ridiculously fast, but acceleration from the Z H2 feels faster because the engine doesn’t need to be revved out as much.
Kawasaki’s supercharger, which debuted on the H2 R at the 2014 Intermot show, is like an afterburner for the 998cc inline-Four. It helps the engine push out almost 200 hp and over 100 lb-ft of torque on the Z H2, while the Ninja H2 churns out as much as 228 hp and the experts-and-track-ready Ninja H2 R makes upwards of 300 hp.
Related: 2015 Kawasaki Ninja H2 First Look Review
Kawasaki reignited interest in superchargers, but the technology has been used on motorcycles for nearly a century. BMW was an early pioneer in the late 1920s, and other manufacturers followed suit prior to World War II. When motorcycle racing resumed in Europe in 1946, the Fédération Internationale de Motocyclisme (FIM) banned superchargers to reduce injuries and deaths, putting forced induction on the backburner until the late 1970s. Imagine going over 150mph with a supercharged engine on a prewar chassis and tires. Yikes.
The Golden Age of Supercharged Motorcycles
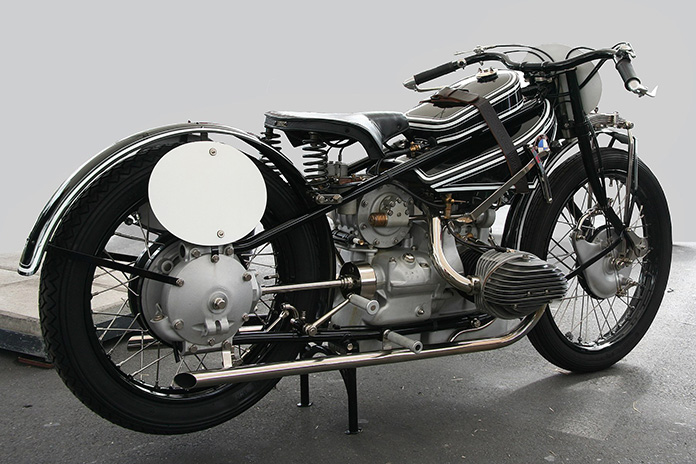
Born from racing, supercharged European motorcycles were the genesis for the evolution of high-performance bikes. American brands like Harley-Davidson and Indian were winning races at home with naturally aspirated engines. BMW started producing motorcycles in 1923, and by the end of the decade, it had developed the WR 750. Powered by a supercharged 4-stroke OHV 750cc boxer Twin, the WR 750 earned BMW a land-speed record at over 134 mph with German racing champion Ernst Henne at the controls.
Related: Riding the Motorcycle Century
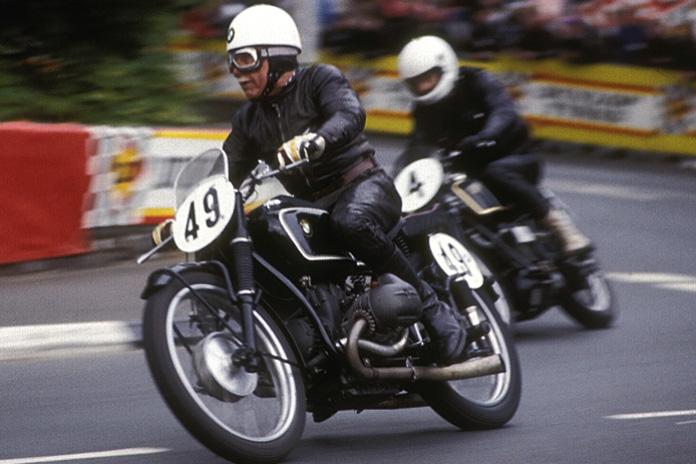

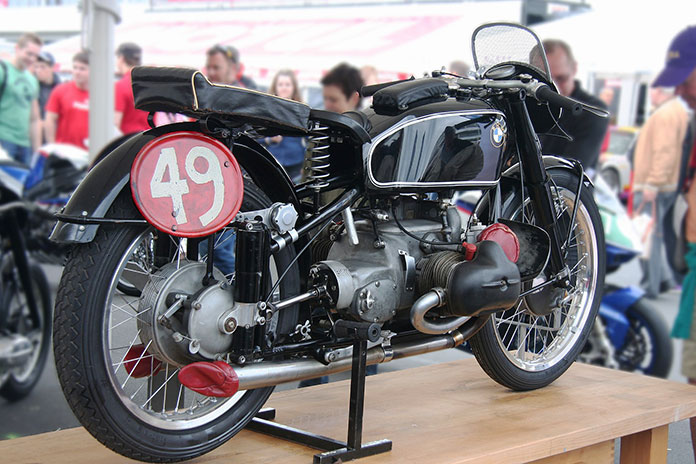
The WR 750 was impressive but couldn’t overcome English dominance at the time, so the BMW Type 255 Kompressor was the next step. In 1939, Georg Meier won the Senior Tourist Trophy race at the Isle of Man on the Type 255, marking the first time a non-English rider had won since 1907. Using a Swiss-made Zoller supercharger, BMW’s 500cc Boxer produced around 60 hp and averaged 89 mph at the race. Meier won the Belgian motorcycle Grand Prix in 1939 as well, becoming the first rider to exceed 100 mph on a lap. The Type 255 was a bona fide superbike for BMW and demonstrated the significant performance advantages of forced induction.
Pre-War Grand Prix
Motorcycle racing was all the rage in the 1930s, and superchargers were common for most European teams. The notable holdout was Norton, which held steady with tried-and-true naturally aspirated Singles. British manufacturer AJS developed a supercharged V-4 monster with a high top speed, but it proved unreliable and either overheated or simply broke down during races. It finally won a race in Belgium in 1946, just before the supercharger ban went into effect.
Luxury French manufacturer Brough Superior developed some of the fastest supercharged bikes of the era. In 1937, Eric Fernihough set a record of 169.79 mph with a supercharged 1,000cc J.A.P. engine in his Brough Superior. Pure insanity at the time, and he was killed the following year chasing another record.
Today, naturally aspirated bikes can exceed 200 hp and still meet Euro 5 emissions standards, which is an incredible testament to how far design and technology have come. Forced induction might seem like overkill, but nothing exceeds like excess. So, what’s the difference between a supercharger and turbo, anyway?
Supercharger
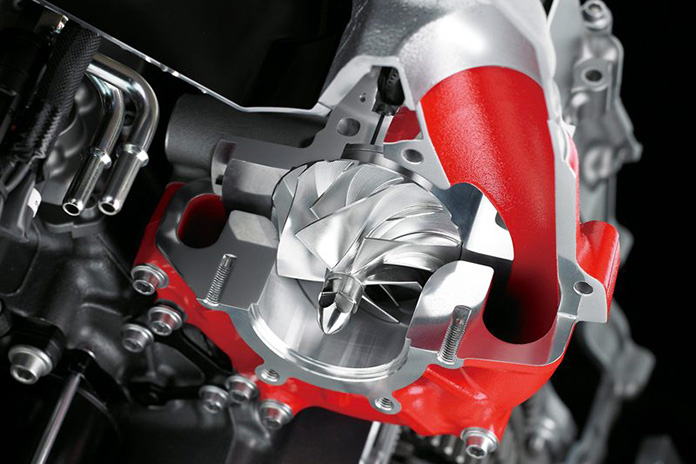
A supercharger is mechanical device that forces more air into the engine to produce more power for a given displacement. In a car, a supercharger is often driven by a belt that wraps around a pulley between the drive and compressor gears. In a modern motorcycle like the Kawasaki H2s, a system of gears connected to the flywheel drives the impeller, which is a metal fan used to compress the intake gas. The impeller must spin much faster than the engine to effectively compress the air. Kawasaki’s supercharger uses planetary gears to spin the impeller up to 130,000 rpm and develops up to 20.5 psi boost pressure.
Turbocharger
Whereas a supercharger is driven by the engine, a turbocharger is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. Wind powered, if you will. The exhaust spins an impeller in the turbo housing, which is connected to a second impeller in the compressor housing that forces additional air into the engine. It can take a moment for the exhaust to get the impeller spinning fast, which creates turbo lag. Superchargers, on the other hand, are always “there,” as the engine is continuously powering them. Turbochargers are relatively lag-free today, but it does persist to varying degrees.
The Golden Age of Turbocharged Motorcycles
1978 Kawasaki Z1R-TC
Unlike the pre-war era fixation on superchargers, the next wave of two-wheeled forced induction was all about turbos, starting in the late 1970s. The Kawasaki Z1R-TC was the first production turbo motorcycle, kicking off what turned out to be a short-lived craze. It had a 1,000cc inline-Four that was a factory authorized conversion of the standard Z1R bikes. A Rajay turbocharger pushed the Z1R-TC to 130 hp (from 94 hp), which was quite a powerhouse in the late ’70s and extreme enough that buyers had to relinquish the factory warranty. It was a bold decision by Kawasaki at the time. Only 250 were built, as they were expensive and complex, but it got the Japanese industry scrambling.
Related: Kawasaki KZ1000 Z1-R TC (Turbocharged): 1978-1979
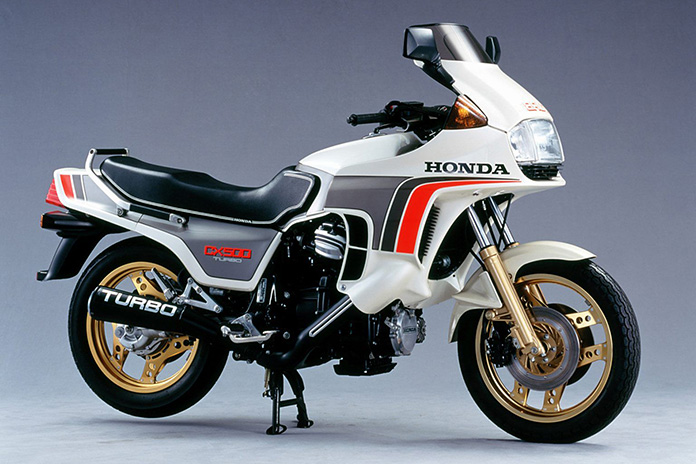
1982 Honda CX500T
Unlike the Z1R-TC, Honda’s first turbocharged bike was born in the factory, and many consider it the first proper factory turbo. I personally give that accomplishment to Kawasaki, but that’s a battle for another day. The water cooled CX500T had an angled, horizontal V-twin inspired by Moto Guzzi and an early fuel injection system, boosted to 80hp by the turbo. Unfortunately, the bike was plagued with turbo lag, so Honda upgraded to a 650cc variant the following year with the CX650. The increased displacement and modified (and lowered) boost brought the new bike to 100 hp, but turbo lag persisted and the price was just too high. These were short lived and disappeared at the end of 1983.
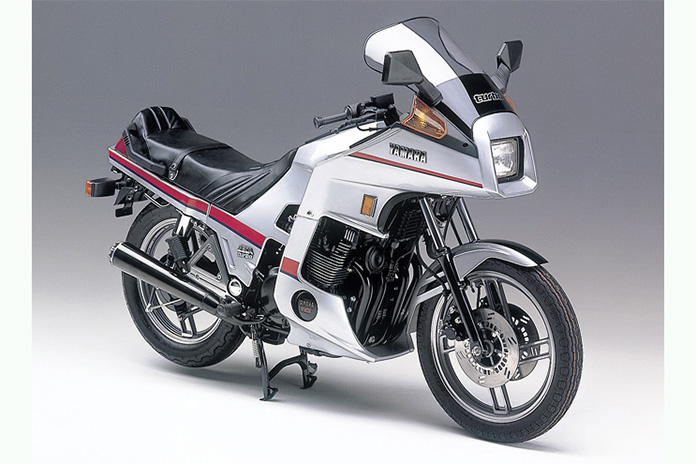
1982 Yamaha XJ650 Turbo
Yamaha released its own turbo soon after Honda, the 90-hp XJ650 Turbo. It was a heavier touring bike in lieu of something more performance oriented. It also wasn’t a ground-up design but rather based on the older XJ650 Seca with a mediocre chassis, drum brakes, and shaft drive, along with outdated Mikuni carburetors. A choppy throttle, bad turbo lag, and lackluster acceleration killed production after two years. Maintenance issues were also bad, as ambition seemed to exceed what was feasible at the time.
Related: Retrospective: Yamaha XJ650RJ Seca 650: 1982
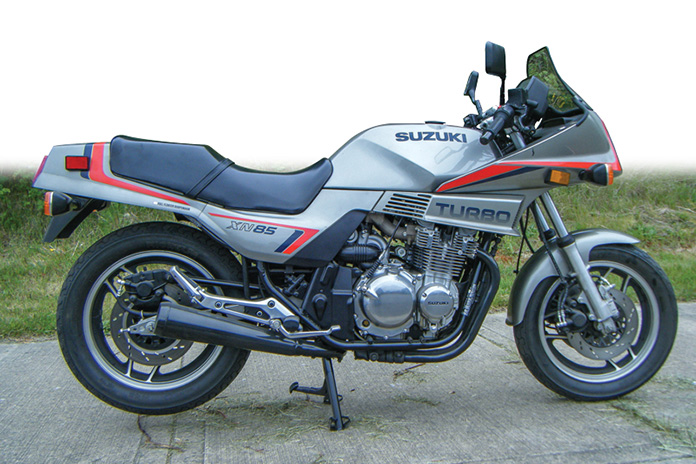
1983 Suzuki XN85
Suzuki’s first turbocharged motorcycle, the XN85 of 1983, was an impressive effort. Like Honda, it was fuel injected, but only oil cooled and pushed out 85 hp. Turbo lag was less than the others, and the chassis was built specifically for the increased power. Like all early turbos, it was complex and expensive to produce, leading to limited production numbers. It did, however, survive for five years, making it the most successful model.
Related: Retrospective: 1983 Suzuki XN85 Turbo
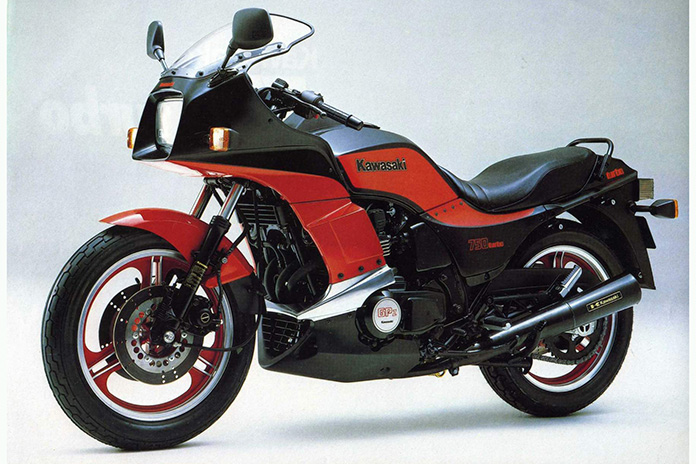
1984 Kawasaki GPz750 Turbo
Six year after the Z1R-TC, Kawasaki introduced the GPz750 Turbo, aka the ZX750-E Turbo. Unlike earlier Japanese efforts that were abandoned at this point, the GPz750 was the real deal. A proper sportbike design held the 738cc inline-Four, which produced 112 hp and was good for 10.71 seconds in the quarter mile. The existing GPz750 engine was heavily modified, and the turbocharged result was the first middleweight that outperformed early ’80s liter bikes. Kawasaki’s GPz1100 sportbike trailed behind the much smaller GPz750 by 3 hp, proving that turbos were serious contenders and not mere novelties. Style, performance, and reliability made this the first truly marketable turbocharged motorcycle and overshadowed all prior efforts. Alas, it was produced for only two years.
Related: Retrospective: 1984-1985 Kawasaki ZX750-E Turbo
Why Did Turbos Fizzle Out?
In less than 10 years, the turbo craze spread like wildfire among the Big Four Japanese manufacturers and burned itself out. The idea was simple and appealing – use forced induction to extract more power out of middleweight engines. But the reality overpromised and underdelivered. Turbochargers proved to be too complex and expensive, and the payoff wasn’t big enough to make them a viable alternative to larger naturally aspirated engines – at least not at the time.
Let’s Get Boosted!

After Japanese manufacturers abandoned turbos, adrenaline junkies continued bolting aftermarket ones to their natural breathers. One of the big names in the business is Trask Performance, which produces turbocharged kits for Harleys that can squeeze 300 hp out of big V-Twins. In my mind, such turbo kits make the most sense on 1,200cc Evo Sportsters that are relatively light and nimble, and the result can more than double the stock power and deliver 120 hp at the rear wheel.
Related: Evo Sportster | End of an Era

Trask isn’t the only company with turbo kits, and versions are available that can be installed on a wide range of motorcycle types and models. Extreme Creations, RCC, Cobalt, and others offer turbochargers that deliver aircraft carrier catapult-caliber launches. You can also buy supercharger kits from companies like Rotrex, ProCharger, and TTS Performance. And if you’re curious, the answer is yes – installing any of them will void your factory warranty.
Turbocharged Suzuki Hayabusa
We can’t review the history of forced induction on motorcycles and overlook a bona fide legend. In 1999, Suzuki introduced the GSX1300R Hayabusa, which won the short-lived top-speed wars of the late ’90s. In stock form, the first-gen 173-hp Hayabusa nearly broke the elusive 200 mph barrier. The second-gen ’Busa got bumped up to 1,340cc and 194 hp, but by then, the OEMs had agreed to impose an electronically limited top speed of 186 mph (300 kph) on its production motorcycles.
Related: 2022 Suzuki Hayabusa | Road Test Review
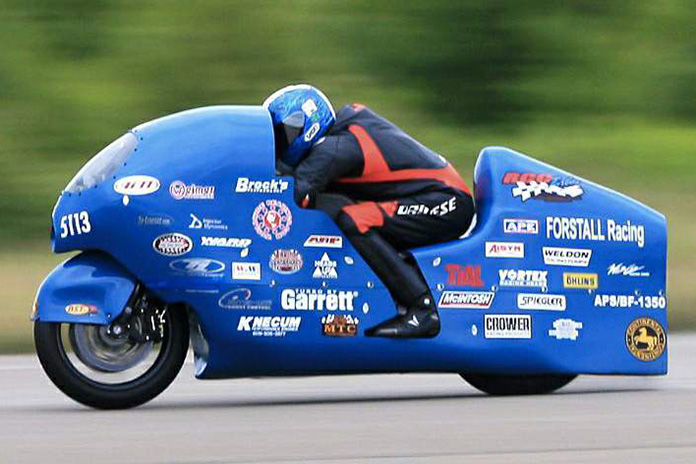
But with some electronic sleight of hand – and a big ol’ turbo – the Hayabusa’s true potential could be unleashed. In 2011, Bill Warner set a motorcycle land-speed record of 311 mph on a streamlined and turbocharged ‘Busa. Add nitrous to the mix, and things just get insane. In 2018, a 1,000-hp ’Busa hit 258.54 mph within 1 mile from a standing start at a Straightliners top-speed event in Yorkshire, U.K.
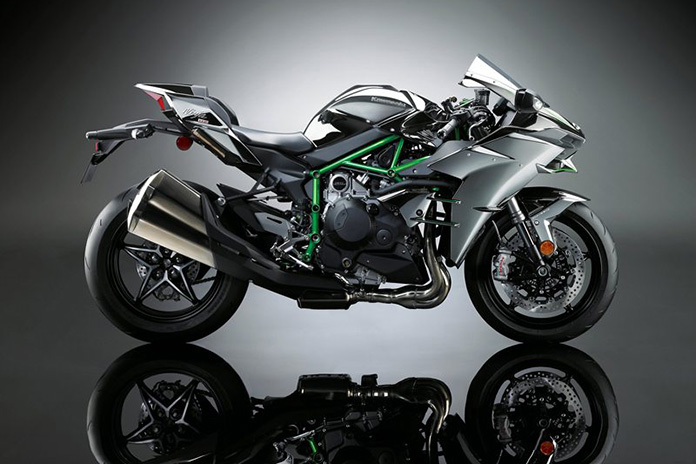
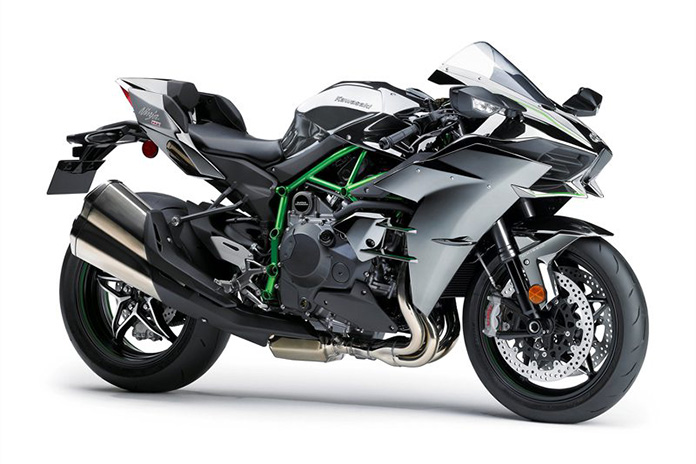
Kawasaki Ninja H2
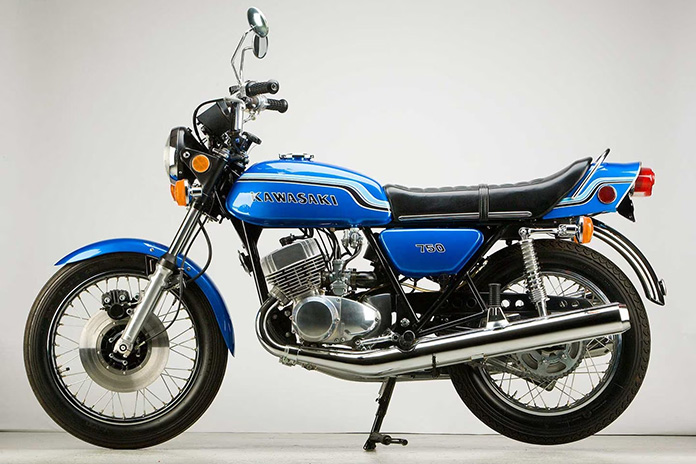
In 2014, we came full circle when Kawasaki introduced the Ninja H2, a factory supercharged sportbike. Over 75 years after superchargers disappeared from European racebikes, Kawasaki resurrected the concept with the most successful lineup of forced-induction motorcycles in modern history. The name comes from Kawasaki’s ’70s-era H2 models powered by 750cc 2-stroke Triples. The 1972 Kawasaki H2 Mach IV, the fastest bike of its day, was known as “the widow maker,” as the chassis and overall design weren’t suited for so much power.
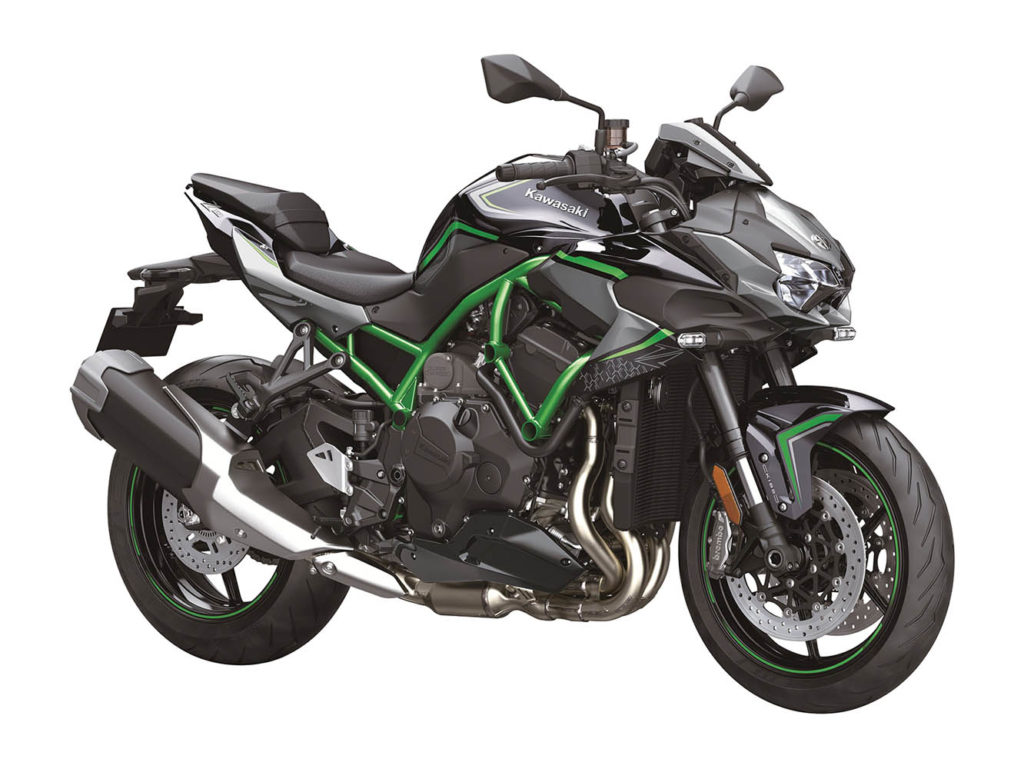
The 2014 Ninja H2 has a 998cc inline-Four with a centrifugal supercharger developed entirely in-house at Kawasaki. The manufacturer had intended to outsource the supercharger, but those plans ultimately called for a bulky intercooler, so Kawasaki brought it under its own roof. The result was an independent and compact unit that boosts a growing H2 portfolio with four bikes in the current lineup: Ninja H2, Ninja H2 R, Ninja H2 SX, and Z H2.
The Ninja H2 and up-spec Ninja H2 Carbon produce a claimed 228 hp and 105 lb-ft of torque, while the track-only H2 R raises the bar considerably with 326 hp and 122 lb-ft of torque. The H2 R is currently the fastest production motorcycle of all time, but it is not street legal. The standard Ninja H2 is heavier than many sportbikes (around 525 lb wet) and won’t handle a track as well as purpose-built machines, but the intensity of acceleration and still competent performance make it one the craziest rides you can buy. With a starting price of $31,500, it’s definitely spendy, but it’s a relative bargain compared to the $56,000 H2 R.
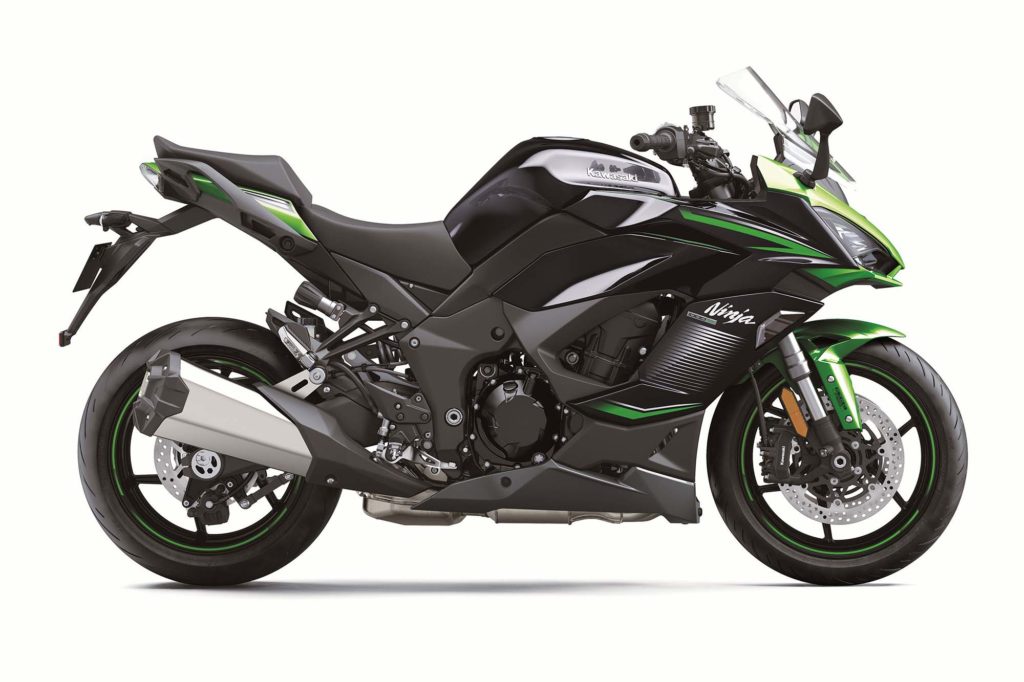
The Ninja H2 SX and Z H2 represent the second-generation of H2 engines, tuned for more real-world conditions with 197 hp and 101 lb-ft of torque. The H2 SX is a sport-touring sportbike with a wet weight over 600 lb, but it still accelerates like a rabid cheetah without having to rev it out.
Related: 2018 Kawasaki Ninja H2 SX SE | Road Test Review
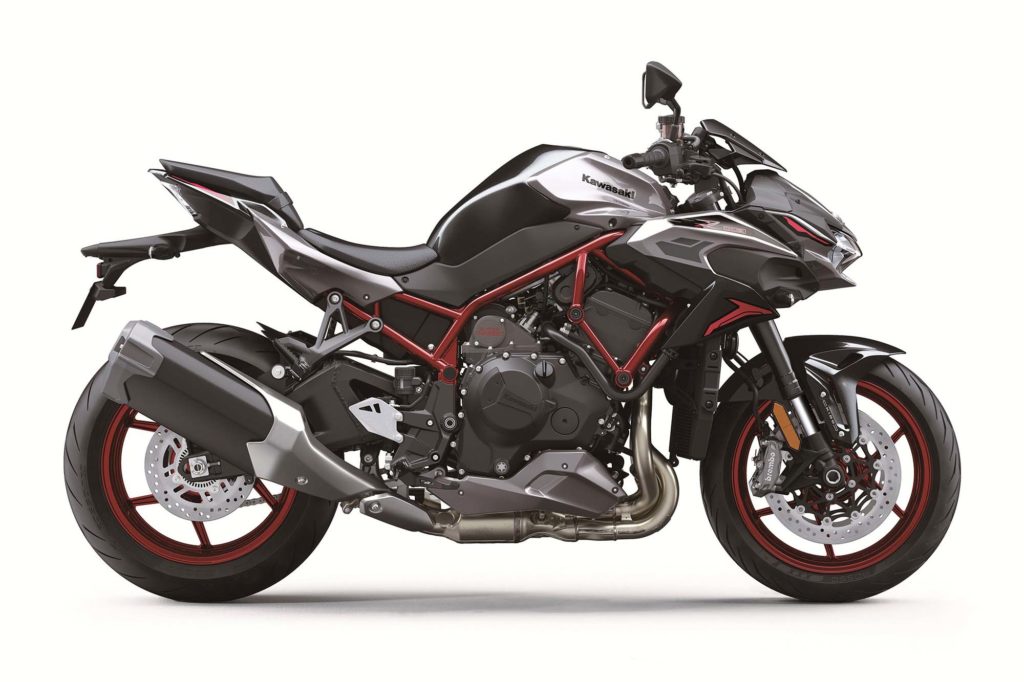
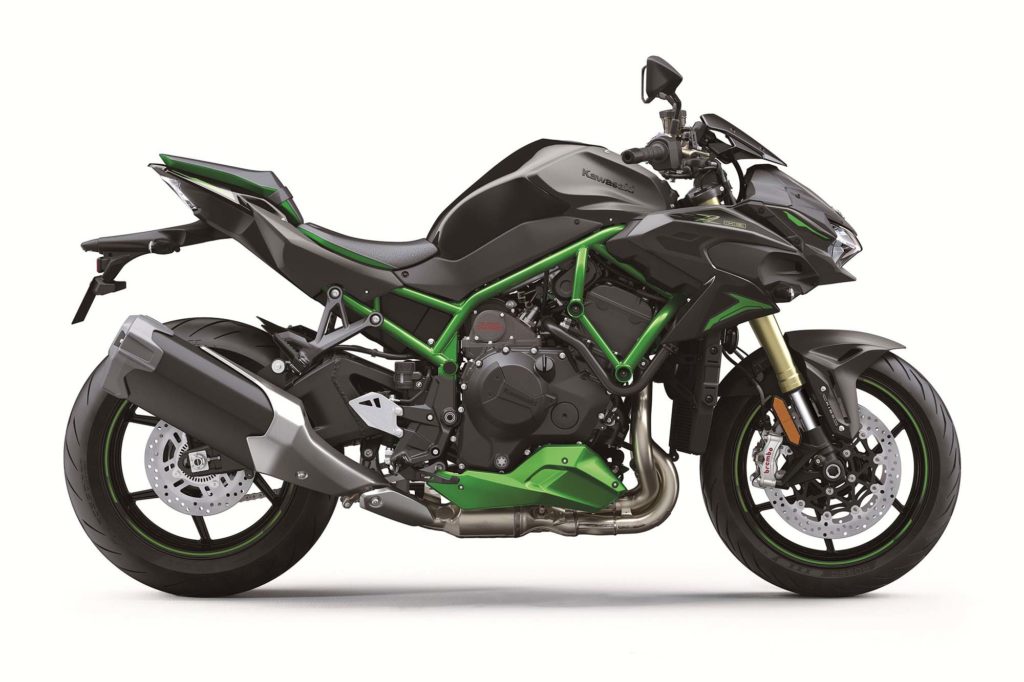
Introduced for 2020, the Z H2 naked bike is the newest model in the H2 lineup, and it’s also the most affordable at $18,500, providing the magic of Kawasaki’s supercharger at a more reasonable price undercutting. It’s not a serious track performer, but it’s not meant to be. It’s a streetbike though and through, and it’s about as fun as it gets with an upright position offering all-day comfort. The up-spec Z H2 SE ($21,700) is equipped with Kawasaki’s Electronic Control Suspension (KECS) and upgraded Brembo calipers, but the core experience is there with the standard model.
Practical Insanity
It’s a bit strange calling a supercharged motorcycle practical, but the Z H2 proves that forced induction can be both affordable and reliable. It certainly qualifies as an everyday bike and is genuinely easy to live with, unlike some high-strung competitors. I don’t know what sorcery went into the supercharger’s design, but Kawasaki nailed it, and a distinctive chirp at deceleration reminds you that you’re riding something special. Supposedly it’s caused by the impeller breaking the sound barrier. We’d like to see a return to the ’80s-era concept of adding forced induction to a middleweight. How cool would it be to see a supercharged version of the Z650, Ninja ZX-6R, or the new Ninja ZX-4RR? Sometimes it’s good when history repeats itself.
The post A Century of Supercharged and Turbocharged Motorcycles first appeared on Rider Magazine.
Source: RiderMagazine.com