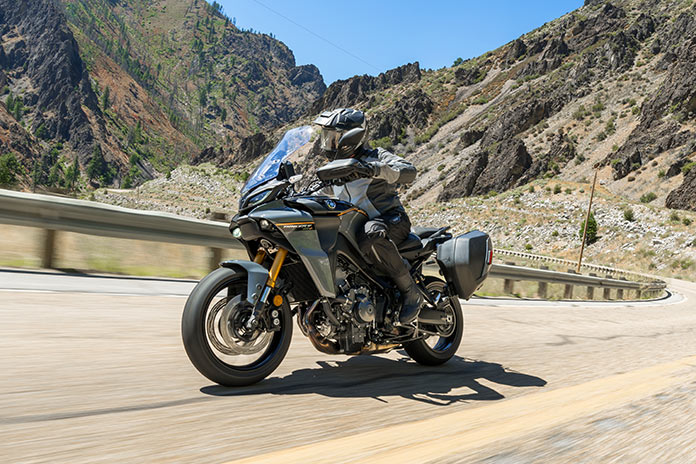
When a bike wins Rider’s Motorcycle of the Year award, as the Yamaha Tracer 9 GT did in 2021, it’s a special machine that beat out dozens of others in the year it was selected. But every motorcycle, even very good ones, can be made better. Just two years after earning MOTY honors, we have the new and improved Yamaha Tracer 9 GT+.
What does the ‘+’ at the end of the name entail? Quite a bit, actually. Tucked under the nose of the Yamaha Tracer 9 GT+ is a new millimeter-wave radar that continuously measures distance to vehicles ahead and enables two features: adaptive cruise control and a radar-linked Unified Brake System. Also new on the GT+ are integrated ride modes, the next generation of the KYB Actimatic Damper System (KADS) electronic suspension, an updated quickshifter, a new 7-inch TFT display with simplified menus, new switchgear, and integration with the Yamaha MyLink and Garmin Motorize smartphone apps.
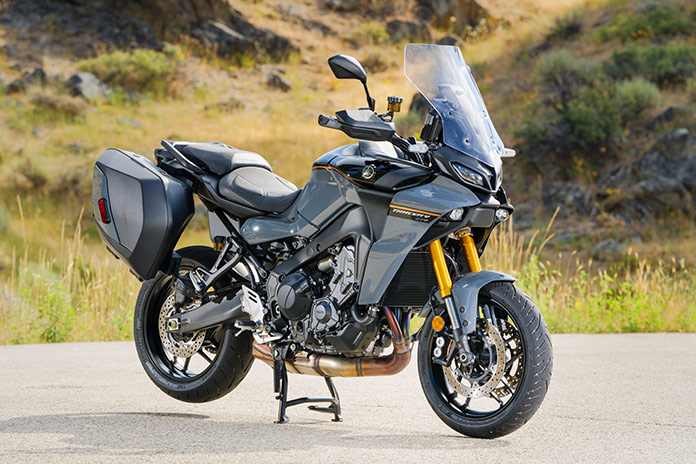

This fourth generation of the Tracer 9 platform – which began with the FJ-09 for 2015 and became the Tracer 900 GT for 2019, the Tracer 9 GT for 2021, and now the Tracer 9 GT+ for 2024 – is about refinement. It adds useful tech and smooths out a few rough edges but retains what has made the FJ/Tracer a Rider favorite for nearly a decade. As we wrote when the Tracer 9 GT won MOTY in 2021, “Thanks to steady evolution and improvement over three generations, Yamaha has demonstrated just how good a modern sport-tourer can be, especially for riders who value agility over couch-like luxury. Performance, sophistication, comfort, versatility, load/luggage capacity – the Tracer checks all the right boxes and leaves nothing on the table.”

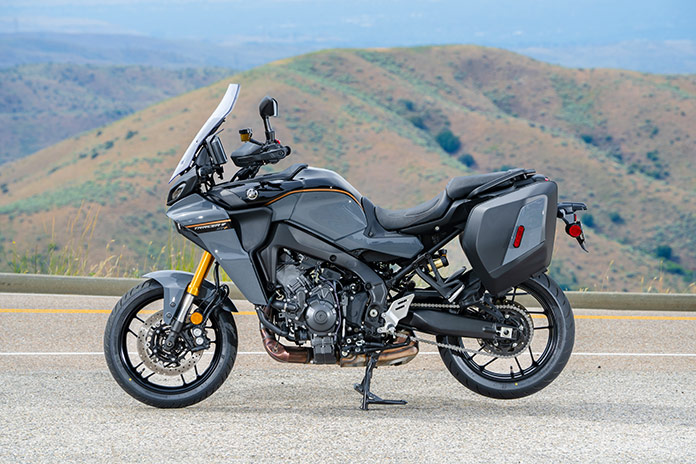
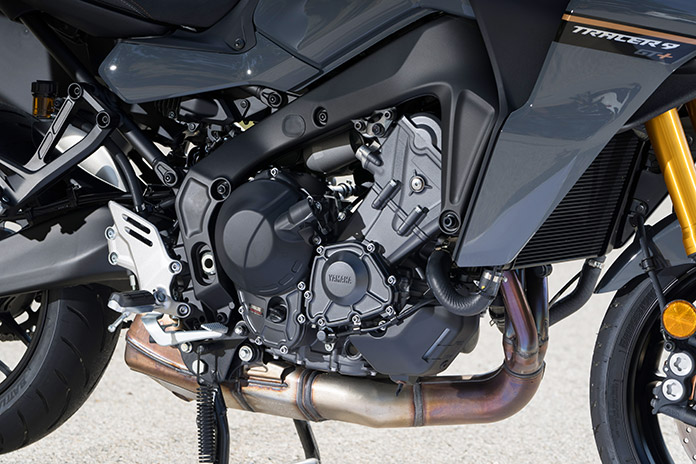
Returning unchanged is the star of the show – the liquid-cooled 890cc CP3 inline-Triple with a crossplane crankshaft, which made 108 hp at 10,000 rpm and 63 lb-ft of torque at 7,200 rpm at the rear wheel on Jett Tuning’s dyno. The CP3 has always been an exciting engine that’s full of character, and it continues to deliver in spades. As before, wrapped around the engine is a controlled-fill diecast Deltabox aluminum frame that is both strong and light. The GT+ also has an aluminum swingarm, a steel subframe, and lightweight spinforged wheels shod with excellent Bridgestone Battlax T32 sport-touring tires. A comprehensive electronics package, 30-liter side cases, LED cornering lights, heated grips, a height-adjustable windscreen, adjustable ergonomics, and many other useful features are all part of the deal.

Since this review takes a deep dive into the new tech, I’ll cut to the chase: The Yamaha Tracer 9 GT+ gets a big gold star for being a fantastic, well-rounded, well-sorted sport-tourer. For this test, I logged over 1,400 miles in three days, and my admiration for the bike deepened with each passing mile. Although its $16,499 MSRP is $1,500 above that of the previous model, the GT+ offers a level of technological sophistication that isn’t available on another motorcycle priced less than $25,000.
Related: Yamaha Announces Updated Ténéré 700, Other Returning 2024 Models
ACC and UBS on the Yamaha Tracer 9 GT+
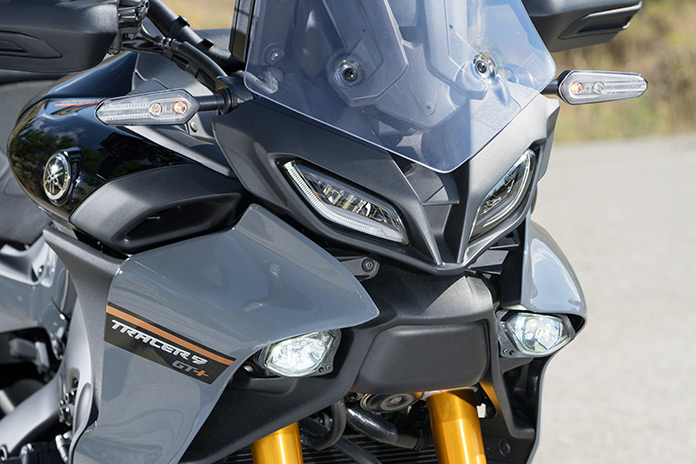

A millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar system emits short-wavelength electromagnetic wave signals that are reflected by objects in their path, allowing the system to determine the distance and velocity of those objects. In the case of the Tracer 9 GT+, the radar detects vehicles ahead in the same lane – it’s unaffected by vehicles going in the same direction in adjacent lanes or approaching vehicles in opposing lanes. When adaptive cruise control (ACC) is engaged, the system shows a car icon if a vehicle is detected within a certain range. If the vehicle ahead is traveling at a slower speed than that set for cruise control, the Tracer will slow to match the lead vehicle’s speed and maintain a set distance. A trigger on the left grip allows the rider to select among four set following distances, ranging from a minimum of one second to a maximum of two seconds. With the mmWave radar box tucked into a central cavity between the headlights and weighing only 7 ounces, it has minimal impact on aesthetics or overall weight.

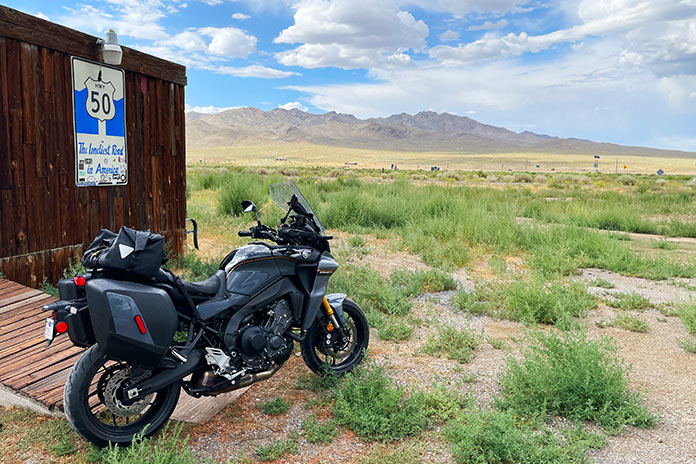
After riding 200 miles around Boise, Idaho, during the one-day press launch, I logged two consecutive 600-mile days riding home to Ventura, California. Day 1 took me due south from Boise through the empty high desert of southwestern Idaho, down into Nevada to Eureka, and across Nevada’s basin-and-range landscape on U.S. Route 50 – “The Loneliest Road in America” – to Carson City. On Day 2, I climbed up the eastern side of the Sierra Nevada range, rode along the shore of Lake Tahoe, crossed into California, and bagged four of the highest paved Sierra passes – Ebbetts (8,730 feet), Monitor (8,314 feet), Sonora (9,624 feet), and Tioga (9,945 feet) – before cruising south on U.S. Route 395 and west on State Routes 14 and 26 to the coast.
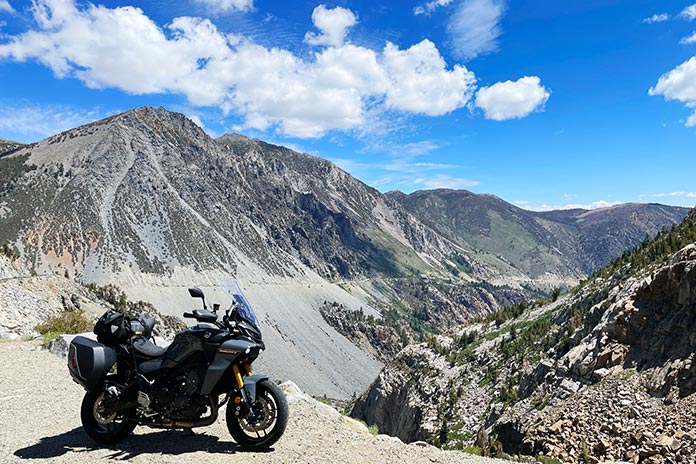

There were few people in these wide-open spaces, and the heaviest traffic I encountered was millions and millions of Mormon crickets that covered some of the roads in Idaho and Nevada for miles. At times I shared the road with a coyote, a few antelopes, and several fast-moving pikas, their tails sticking straight up in the air as they scurried across the hot asphalt. Temperatures ranged from 50 to 100 degrees, and several desert rainstorms provided cooling relief from the summer heat.

I’ve never been a heavy user of cruise control – I’d use it occasionally to give my right arm a break, to do some stretches, or to keep the bike at a steady speed while I opened or closed vents in my jacket – but I disliked having to disengage and re-engage cruise control when I came upon other vehicles in my lane. But I used adaptive cruise control for much of my 1,200-mile trip home. I’d set it to avoid the speed creep that can happen on long rides, sometimes leading to unpleasant interactions with the local constabulary. When I’d come upon a vehicle ahead of me, ACC would adjust the bike’s speed using engine braking, and then, if necessary, the front and rear brakes. If I changed lanes to overtake the vehicle, ACC would accelerate to the set speed.

ACC works from 20-99 mph in all gears, and only if traction control, slide control, and (front wheel) lift control are turned on (which they are by default in all ride modes). When using ACC’s acceleration and deceleration toggle switch, speed can be adjusted in 1-mph or 5-mph increments. Furthermore, using inputs from the 6-axis IMU (inertial measurement unit), ACC employs cornering assist (limits acceleration when leaned over), passing assist (smooths acceleration when the turnsignal is on), KADS integration (adjusts suspension damping to limit chassis pitch), and a rider warning system if following distance is too close. While all the different features of ACC may make it sound complicated, in practice it is very intuitive to use. ACC, however, is not a collision avoidance system or some sort of autopilot; the rider needs to stay engaged at all times.
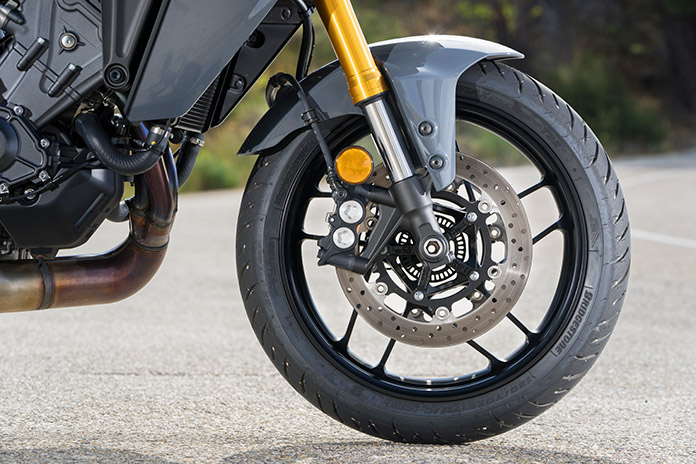

The mmWave radar system also enables a radar-linked Unified Brake System that Yamaha says is a world-first technology on the Tracer 9 GT+. Using inputs from the IMU, suspension control unit, and engine control unit, the system adjusts braking and suspension forces to help keep the motorcycle under control. If the rider applies the brakes and the radar system detects an object or vehicle in the road, UBS will apply additional front/rear braking as needed, and compression damping will be increased to prevent chassis pitch. The Brake Control (cornering ABS) system must be turned on, and UBS works whether or not ACC is engaged. UBS is not an emergency braking system; it provides assistance only if the rider is already on the brakes. To support UBS and improve overall braking performance, Yamaha increased the diameter of the Tracer’s rear brake disc from 245mm to 267mm and made the rear brake pedal slightly wider with a more beveled shape.

GEAR UP
- Helmet: Schuberth E2 Modular
- Jacket: Fly Racing CoolPro Mesh
- Gloves: Fly Racing Brawler
- Pants: Fly Racing CoolPro Mesh
- Boots: Fly Racing Milepost
I used ACC for many hours of my two-day ride home, and how it worked when I approached or passed other vehicles on the road was obvious. Perhaps because there was little traffic on the road, I don’t recall any moments of hard or abrupt braking that would have engaged the radar-linked UBS function. An icon will flash on the TFT display, similar to a traction control light flickering when rear wheel spin is being managed, but I didn’t see such an icon. Then again, if I’m braking hard to avoid hitting something, I’m focused on the road and not on the dash.
Other New New on the Yamaha Tracer 9 GT+
Whereas ACC and UBS are new features, other updates refine existing ones. The quickshifter previously allowed clutchless upshifts during acceleration and clutchless downshifts during deceleration. On the GT+, the quickshifter also allows upshifts during deceleration (e.g., to limit engine braking) and downshifts during acceleration (e.g., to assist with making a pass). Also, the quickshifter can be used when ACC is engaged.
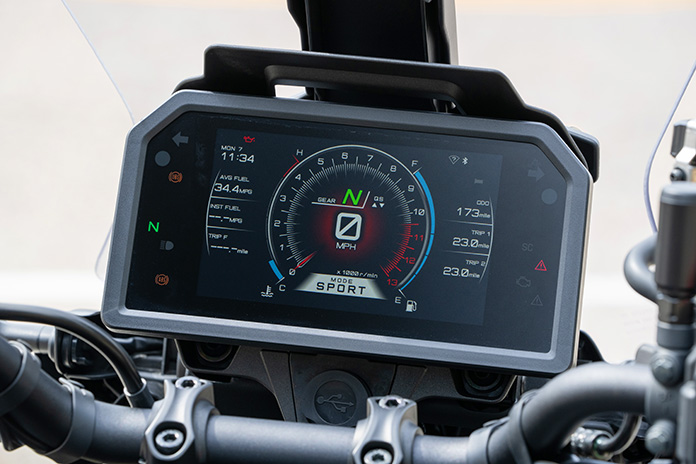

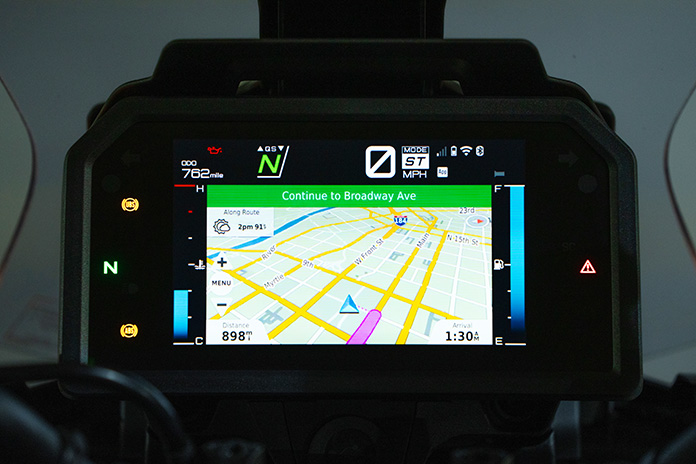
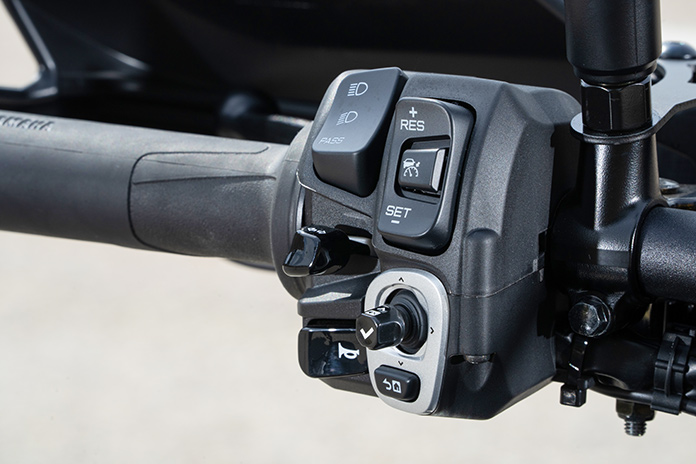
From a user-interface perspective, two of the best upgrades on the Tracer 9 GT+ are the move from a pair of 3.5-inch TFT displays to a single 7-inch TFT display and revised switchgear. The TFT has crisp, full-color graphics, three display modes, and an anti-glare coating that makes the screen legible even in bright sunlight. Simplified menu systems are more intuitive than before, and the joystick and home button on the left grip make navigating between screens, menus, and functions easy (though occasionally I’d mistake the joystick for the turnsignal switch, which is just to the left of it). All the switches have ergonomic shapes, a tactile feel, and new backlighting.

The Tracer 9 GT+ offers Bluetooth connectivity, allowing a smartphone and up to two headsets to be connected to the bike for controlling music and phone calls. The free Yamaha MyLink app allows text messages and incoming call info to be displayed on the dash, provides weather info and alerts, and allows use of the Garmin Motorize navigation app (subscription required – $4.99/month or $39.99/year). I used both, and Garmin Motorize was especially useful because it displayed Garmin’s familiar GPS screen right on the TFT display, eliminating the hassle of mounting a separate GPS unit or my smartphone on the bike for navigation. Using the Garmin app, however, was a drain on my iPhone’s battery, going from 100% to about 50% in just a few hours. There is a USB-A outlet just below the dash, so I ran a charging cord from the outlet to the phone in my pocket as needed.
As much as I liked the features and capabilities of the Yamaha MyLink and Garmin Motorize apps, I do have a couple nits to pick. First, the Yamaha app must be paired to a smartphone via wi-fi, but when the bike is shut down (such as removing the key to open the fuel filler) and then turned back on, the bike and Yamaha MyLink app wouldn’t always reconnect automatically. Sometimes it would be just a matter of opening the app and tapping the paired device button to reestablish the connection. But occasionally it would connect and then quickly disconnect, saying “communication error.” I’d get stuck in a connect/disconnect loop until finally the app and the bike decided to start talking to each other again. When on the side of the road after a photo stop or at a gas station during a long day’s ride, such connectivity issues can be frustrating.

My other nit to pick may reflect my personal proclivities and be completely irrelevant to others. When the Garmin Motorize app is being used, a long press of the home button on the left grip switches between the main screen and the navigation screen (a short tap of the home button brings up other functions). When the navigation screen is up, only limited vehicle information is displayed: coolant temperature on the left, fuel level on the right, and along the top, speed, ride mode, gear position, quickshifter status, and one of only four data points: odometer, tripmeter 1, total travel time, and clock, which can be scrolled through using the joystick. One of my favorite data points is ambient temperature, but it’s not available on that screen.

When adaptive cruise control is engaged, ACC info replaces the engine temperature gauge on the left side of the navigation screen. Switching over to the main screen, ACC info is also shown on the left, and it replaces the vehicle info that is normally displayed on the left side of the screen. On the right side of the screen, the rider can choose three vehicle info “favorites” from among the following: ambient temperature, coolant temperature, average speed, tripmeter 1, tripmeter 2, total trip time, average mpg, instant mpg, and low-fuel tripmeter (which begins counting once low-fuel warning comes on). Three of the remaining vehicle info data points are shown on the left, and the rest can be scrolled through using the joystick but their order can’t be changed. And when ACC is engaged, the remaining vehicle info data points are not available.
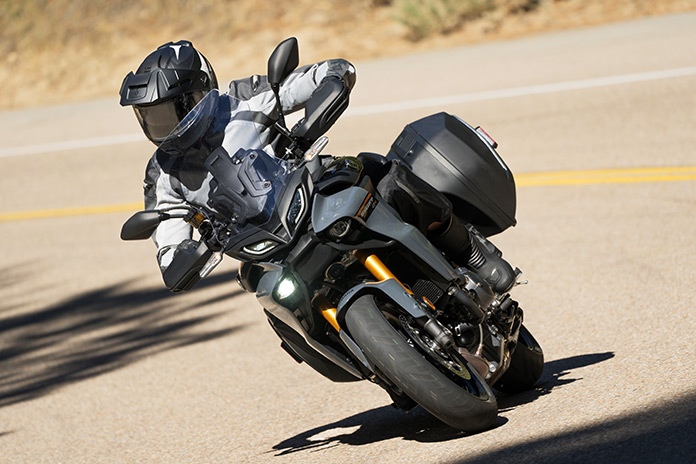

Riding the Yamaha Tracer 9 GT+
Whew, that was a lot of technical info! But for those who are interested in keeping abreast of new technology, we do our best to report them. Now comes my favorite part of the review: what it’s like to ride the Yamaha Tracer 9 GT+.
As mentioned, the Tracer’s 890cc Triple is a gem of an engine. Yamaha’s “crossplane concept” design means that each crankpin is offset 120 degrees from the next, and the three cylinders fire sequentially (1-2-3) in even 240-degree intervals. The engine is versatile, remaining smooth and docile at low revs and cruising along at highway speeds with minimal vibration, but it’s ready to party with a quick twist of the throttle. Horsepower builds linearly to its peak at 10,000 rpm, while torque holds steady: 54-63 lb-ft between 3,000 and 10,200 rpm (redline is 10,500). With a max of 108 hp, the Tracer doesn’t launch out of corners like an open-class sport-tourer, but keeping revs in the sweet spot between 6,000 and 9,000 rpm will please all but the greediest power addicts.
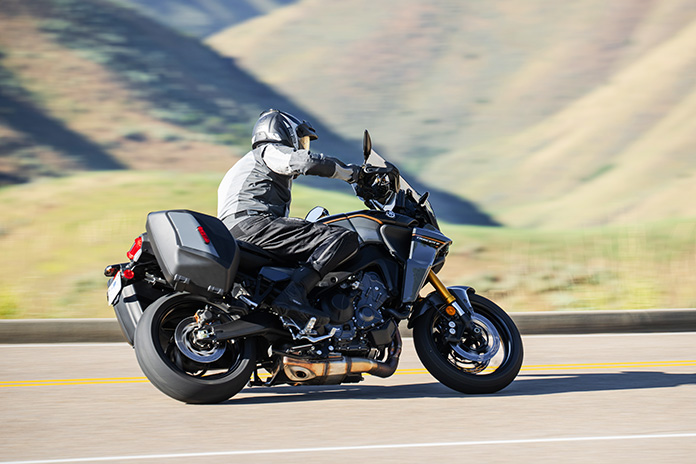

Rather than power modes (four), suspension modes (two), and electronic rider aids (traction control, slide control, and lift control) that must be adjusted separately as on the previous model, Yamaha made the Tracer 9 GT+ more user-friendly by giving it integrated ride modes with intuitive names and presets for all of the above: Sport, Street, Rain, and a Custom mode for those who like to tinker with settings.
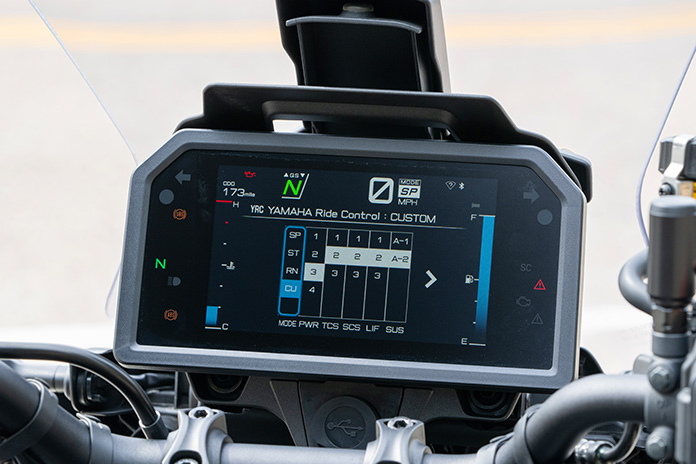

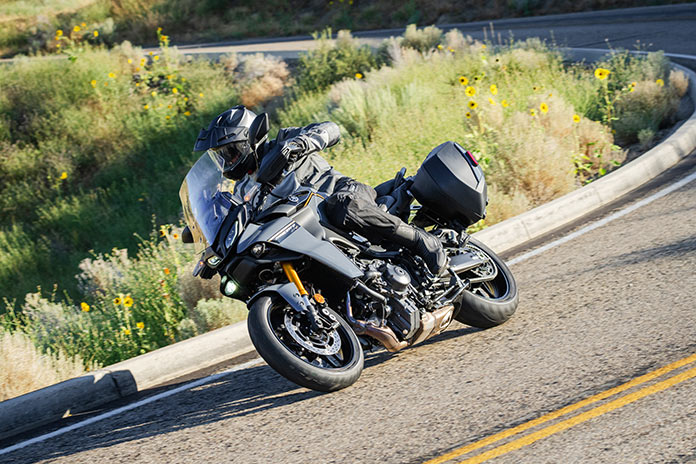
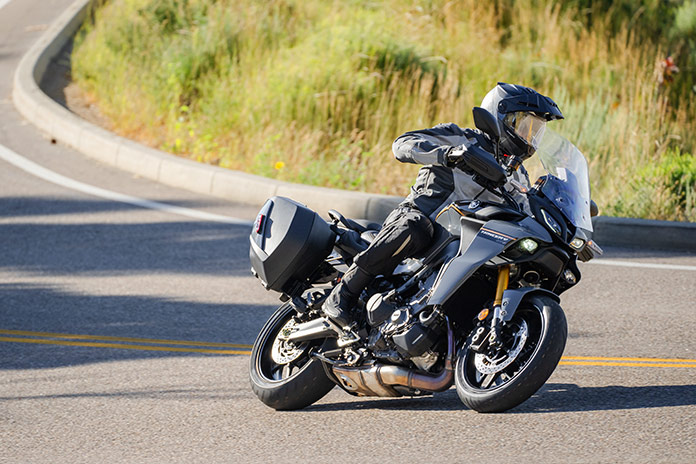
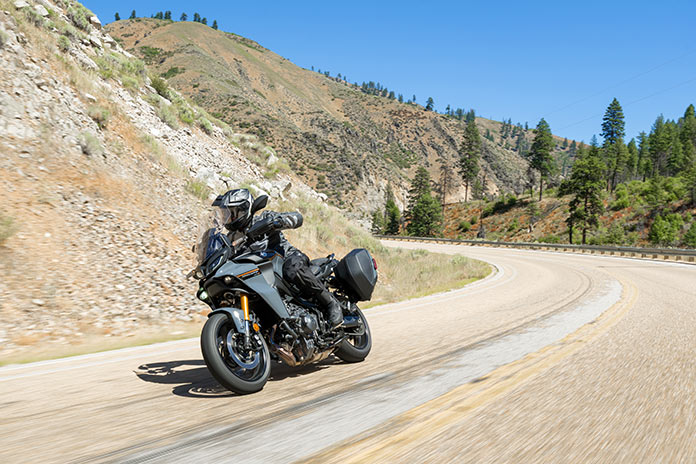
With an upright seating position more like an adventure tourer than a traditional sport-tourer, the Tracer 9 GT+ is comfortable for long rides and allows the rider to quickly adopt an attack stance as needed, with the wide handlebar offering ample steering leverage. With a curb weight below 500 lb, a robust chassis, and frame geometry that favors agility, the Tracer loves to dive into and out of curves and responds obediently to small inputs. Strong, responsive brakes shed speed with good feedback or stop quickly as needed, and the 6-speed transmission changes gears effortlessly with either the slip/assist clutch or the quickshifter. The adjustable windscreen and standard hand guards provide good wind protection, and the revised seat, which has a new shape and cover, is reasonably comfortable but could use more support for long days in the saddle.
We’ve been heaping praise on the FJ/Tracer platform for years, while also pointing out flaws. With each new generation, Yamaha has addressed many of those flaws while also raising the bar in terms of performance, technology, safety, and convenience. If Rider selected a Motorcycle of the Decade, the Tracer 9 GT+ would be on the short list.
2024 Yamaha Tracer 9 GT+ Specifications
- Base Price: $16,499
- Warranty: 1 yr., unltd. miles
- Website: YamahaMotorsports.com
ENGINE
- Type: Liquid-cooled, transverse inline-Triple, DOHC w/ 4 valves per cyl.
- Displacement: 890cc
- Bore x Stroke: 78.0 x 62.1mm
- Compression Ratio: 11.5:1
- Valve Insp. Interval: 26,600 miles
- Fuel Delivery: EFI w/ YCC-T & 41mm throttle bodies x 3
- Lubrication System: Wet sump, 3.4 qt. cap.
- Transmission: 6-speed, cable-actuated wet slip/assist clutch & up/down quickshifter
- Final Drive: O-ring chain
CHASSIS
- Frame: Cast aluminum w/ engine as stressed member, cast aluminum swingarm & steel subframe
- Wheelbase: 59.1 in.
- Rake/Trail: 25 degrees/4.3 in.
- Seat Height: 32.3/32.9 in.
- Suspension, Front: 41mm inverted fork, electronically adj. rebound & compression, manually adj. preload, 5.1 in. travel
- Rear: Single shock, electronically adj. rebound, manually adj. preload (remote), 5.4 in. travel
- Brakes, Front: Dual 298mm discs w/ 4-piston radial calipers & ABS
- Rear: Single 267mm disc w/ 2-piston caliper & ABS
- Wheels, Front: Cast, 3.50 x 17 in.
- Rear: Cast, 5.50 x 17 in.
- Tires, Front: 120/70-ZR17
- Rear: 180/55-ZR17
- Wet Weight: 492 lb
- Load Capacity: 407 lb
- GVWR: 910 lb
PERFORMANCE
- Horsepower: 108 @ 10,000 rpm (rear-wheel dyno)
- Torque: 63 lb-ft @ 7,200 rpm (rear-wheel dyno)
- Fuel Capacity: 5.0 gal.
- Fuel Consumption: 45.9 mpg
- Estimated Range: 230 miles
The post 2024 Yamaha Tracer 9 GT+ Review | Road Test appeared first on Rider Magazine.
Source: RiderMagazine.com